Understanding the technical specifications of the Solana blockchain. – Understanding the technical specifications of the Solana blockchain, we’ll dive into the intricacies of this high-performance blockchain. Solana’s unique approach to consensus, transaction processing, and network architecture sets it apart from other platforms. We’ll explore its Proof-of-History (PoH) mechanism, the role of components like Turbine and Sealevel, and the strategies employed for achieving remarkable scalability and speed. Get ready to unravel the technical magic behind Solana’s impressive capabilities.
This exploration will cover key aspects including Solana’s consensus mechanism, transaction processing pipeline, network architecture, smart contract capabilities, tokenomics, security features, interoperability, and future roadmap. We’ll compare Solana to other blockchains, examine its strengths and weaknesses, and offer insights into its potential for future growth and development. By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of what makes Solana tick.
Tokenomics and Governance
Solana’s success hinges on its robust tokenomics and governance model, which incentivizes network participation and ensures its long-term stability. Understanding how the SOL token functions and how community members participate in governance is crucial to grasping the overall health and future of the Solana ecosystem.
The Solana token (SOL) serves as the lifeblood of the Solana network, playing a vital role in its security and governance. It’s used for transaction fees, staking to secure the network, and participating in on-chain governance proposals.
SOL Token’s Role in Network Security and Governance
SOL’s primary function is to secure the network through staking. Validators, who are responsible for verifying and adding transactions to the blockchain, must stake a significant amount of SOL. This incentivizes them to act honestly and efficiently, as losing staked SOL due to malicious activity or poor performance is a significant penalty. Beyond security, SOL also grants holders voting rights in Solana’s on-chain governance system, allowing them to influence the direction of the network’s development.
Staking SOL and Network Governance Participation
Staking SOL is a straightforward process that involves locking up your tokens in a validator’s node. Validators are chosen based on their staked amount and performance. In return for staking, you earn rewards in SOL, proportional to the amount staked and the validator’s performance. These rewards incentivize participation in network security. Furthermore, the amount of SOL staked directly correlates to your voting power in governance proposals.
These proposals can range from protocol upgrades to changes in network parameters. This direct participation allows token holders to actively shape the future of Solana.
Solana’s Tokenomics
Solana’s tokenomics are designed to balance network security, incentivize participation, and ensure long-term sustainability. The following table summarizes key aspects:
| Aspect | Description | Impact on Network | Future Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Staking Rewards | Rewards paid to validators for securing the network and to delegators for participating in staking. | Incentivizes participation in network security, ensuring network stability and reliability. | Continued staking rewards are crucial for attracting and retaining validators, maintaining network security, and potentially influencing inflation rates. |
| Transaction Fees | Fees paid by users for transactions on the Solana network. | Provides a revenue stream for the network and incentivizes efficient transaction processing. | Transaction fees could potentially be used to fund network development or community initiatives, further strengthening the ecosystem. |
| Inflation | A controlled rate of SOL token creation to incentivize staking and network growth. | Provides a steady supply of SOL for staking rewards and network development, while potentially impacting the token’s value. | Careful management of inflation is vital to maintain the value of SOL and prevent excessive dilution. The rate may adjust over time based on network needs. |
| Governance Voting | SOL holders can vote on proposals impacting the network’s future. | Allows for community-driven development and ensures the network evolves to meet user needs. | Decentralized governance empowers the community and fosters innovation, leading to a more resilient and adaptable network. |
Security and Resilience: Understanding The Technical Specifications Of The Solana Blockchain.

Solana’s design prioritizes both security and resilience, aiming for a robust and dependable blockchain network. This involves a multi-layered approach encompassing various security mechanisms and strategies to mitigate potential threats and ensure network uptime. Understanding these aspects is crucial for appreciating Solana’s overall functionality and its position within the broader cryptocurrency landscape.Solana employs a combination of cryptographic techniques and network protocols to safeguard against common blockchain vulnerabilities.
Its consensus mechanism, Proof of History (PoH), plays a vital role in enhancing security by providing a verifiable timestamping mechanism, making it more difficult for attackers to manipulate the blockchain’s history. Furthermore, the network’s architecture incorporates features designed to detect and respond to malicious activities, minimizing the impact of potential attacks.
Security Measures Implemented in Solana
Solana utilizes a variety of security measures to protect against various attack vectors. These include robust cryptography for securing transactions and accounts, network-level defenses against denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, and regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. The network’s decentralized nature also inherently enhances security, making it more resistant to single points of failure. The use of a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, combined with PoH, further strengthens security by requiring validators to stake a significant amount of SOL tokens, disincentivizing malicious behavior.
This staked capital acts as a deterrent against attacks that could compromise the network’s integrity.
Handling Network Failures and Ensuring Resilience
Solana’s architecture is designed to handle network failures gracefully and maintain network uptime. The network employs various redundancy mechanisms, including geographically distributed nodes and automated failover systems, ensuring that the network continues to function even in the event of node outages or network partitions. Furthermore, the network’s consensus mechanism is designed to tolerate a certain degree of network latency and node failures without compromising the integrity of the blockchain.
Solana’s developers continuously work on improving the network’s resilience through ongoing software updates and infrastructure improvements. This proactive approach aims to minimize downtime and maintain the network’s overall stability.
Examples of Past Security Incidents and Lessons Learned
While Solana has generally demonstrated good resilience, it has experienced some network outages and security incidents in the past. These incidents, while disruptive, have provided valuable learning opportunities and driven improvements to the network’s security and stability. For example, a significant network outage in September 2022 resulted from a combination of factors, including high transaction volume and network congestion.
This event highlighted the need for continued scaling improvements and more robust network management strategies. The subsequent analysis and remediation efforts led to substantial improvements in network capacity and resilience, resulting in fewer similar incidents. The community’s response and collaboration with the Solana Foundation were key in addressing these issues and learning from them. The network has subsequently implemented various upgrades and improvements to prevent similar disruptions in the future.
Interoperability and Ecosystem

Solana’s success hinges not only on its internal capabilities but also on its ability to connect and collaborate with other blockchains and foster a thriving ecosystem of decentralized applications (dApps). This section explores Solana’s interoperability strategies and the vibrant ecosystem it has cultivated.Solana’s approach to interoperability is multifaceted. While not directly implementing cross-chain bridges in its core protocol, it actively supports and encourages the development of various bridging solutions.
These bridges allow for the transfer of tokens and data between Solana and other networks, expanding its utility and reach. The robust nature of the Solana network, with its high transaction throughput and low latency, makes it an attractive destination for projects seeking a scalable and performant platform. Furthermore, the Solana Foundation actively invests in and collaborates with projects developing interoperability solutions, further solidifying its position in a multi-chain future.
Solana’s Interoperability Mechanisms
Solana’s interoperability isn’t a single, built-in feature, but rather a collection of approaches and partnerships. Several projects have built bridges connecting Solana to other major blockchains like Ethereum, Cosmos, and others. These bridges use various techniques, often involving wrapped tokens (representing assets from one chain on another) and secure communication protocols to facilitate asset transfers and data exchange. The security and efficiency of these bridges are critical, and continuous improvements and audits are essential to maintaining trust and preventing exploits.
The Solana Foundation actively monitors and supports the development of secure and reliable bridge technologies.
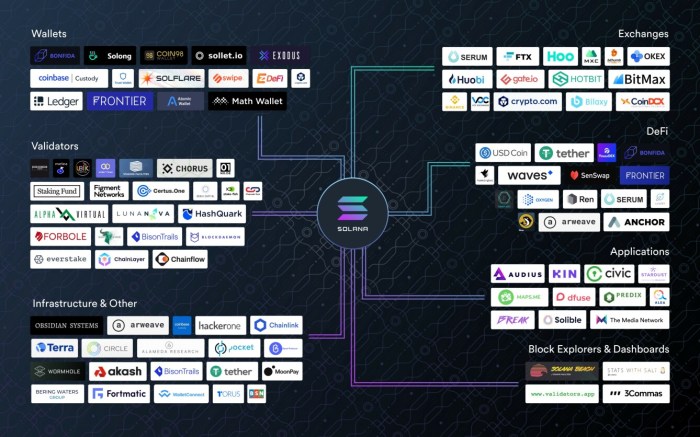
The Solana Ecosystem of Applications and Projects
The Solana ecosystem boasts a diverse range of applications and projects, showcasing its versatility and potential. From decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols to non-fungible token (NFT) marketplaces and gaming platforms, Solana supports a wide array of use cases. The ecosystem’s growth is driven by a combination of factors, including its performance, developer-friendly tools, and a supportive community. The active engagement of developers and the continuous influx of new projects are key indicators of the ecosystem’s health and long-term sustainability.
Key Projects and Applications in the Solana Ecosystem, Understanding the technical specifications of the Solana blockchain.
The following list highlights some notable projects built on the Solana blockchain, demonstrating the breadth and depth of its ecosystem. This is not an exhaustive list, and new projects are constantly emerging.
- Serum: A decentralized exchange (DEX) offering high-speed trading and low fees.
- Raydium: Another popular DEX on Solana, known for its automated market maker (AMM) functionality.
- Magic Eden: A leading NFT marketplace specializing in Solana-based NFTs.
- Solana Pay: A payment protocol enabling seamless and low-cost transactions using Solana.
- StepN: A move-to-earn application leveraging Solana’s scalability for its large user base.
- Marinade Finance: A liquid staking protocol allowing users to stake their SOL tokens and earn rewards while maintaining liquidity.
- Jito: A decentralized social media platform built on Solana.
Future Developments and Roadmap
Solana’s future hinges on its ability to address current limitations while capitalizing on emerging technological trends. The roadmap involves continuous improvement of scalability, security, and developer tooling, aiming to solidify its position as a leading blockchain platform. This involves a multifaceted approach, incorporating community feedback and anticipating future market demands.Solana’s planned developments are ambitious, aiming to significantly enhance the platform’s capabilities and address past challenges.
This involves a complex interplay of technical upgrades, ecosystem expansion, and community engagement. Understanding these planned improvements is crucial for assessing Solana’s long-term viability and potential.
Planned Upgrades and Enhancements
Solana’s development team consistently releases updates and improvements. These range from performance optimizations to new features designed to improve the developer experience and attract new users. Recent examples include enhancements to its consensus mechanism to improve transaction throughput and latency. Future upgrades may include improved cross-chain interoperability, further decentralized governance mechanisms, and enhanced tooling for smart contract development.
These developments are often announced on the Solana blog and through official channels.
Challenges and Opportunities
Solana faces several challenges, including the need to maintain network stability and security in the face of increasing transaction volume. Competition from other Layer-1 blockchains also presents a significant challenge. However, opportunities abound, including the growing demand for decentralized applications (dApps), the expansion of the NFT market, and the increasing adoption of Web3 technologies. Solana’s ability to adapt to these changing dynamics will be crucial for its future success.
For example, the successful integration of new decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols could significantly boost its adoption and market share.
Hypothetical Future Scenario (5 Years)
In five years, Solana could be a dominant force in the blockchain space, boasting significantly improved scalability and security. Imagine a scenario where Solana’s transaction throughput has increased tenfold, enabling it to handle millions of transactions per second. Its ecosystem might be home to thousands of thriving dApps, ranging from DeFi protocols to metaverse applications and supply chain management tools.
Solana’s improved interoperability could lead to seamless integration with other prominent blockchains, facilitating the flow of data and assets across different networks. This enhanced scalability and interoperability, combined with a robust and secure network, could place Solana in a strong position to compete with established players and emerging contenders. This success, however, would depend on continued innovation, community support, and successful navigation of regulatory hurdles.
A successful implementation of improved governance mechanisms could also foster a more inclusive and participatory ecosystem. This scenario assumes continued investment in research and development, as well as a growing adoption of blockchain technology by mainstream users and businesses.
Solana’s innovative technology, combining Proof-of-History with a carefully designed architecture, enables impressive transaction speeds and scalability. While challenges remain, Solana’s commitment to innovation and its vibrant ecosystem position it as a significant player in the blockchain landscape. Understanding its technical underpinnings is crucial for anyone looking to develop on or invest in this rapidly evolving platform. This deep dive has hopefully armed you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of Solana and its potential.