The potential use of blockchain technology in identity management. – The potential use of blockchain technology in identity management is revolutionizing how we think about digital identity. Imagine a world where your personal data is secure, private, and entirely under your control. Blockchain, with its decentralized and immutable ledger, offers a promising path towards this vision. This technology empowers individuals with greater autonomy over their digital identities, enhancing security and streamlining various processes across multiple sectors.
This exploration delves into the core principles of decentralized identity management using blockchain, examining its advantages over traditional centralized systems. We’ll compare different blockchain-based solutions, discuss data security and privacy enhancements, and address the challenges of interoperability and standardization. Real-world applications, scalability concerns, and the legal landscape will also be explored, painting a comprehensive picture of blockchain’s transformative potential in the realm of identity management.
Scalability and Performance Considerations
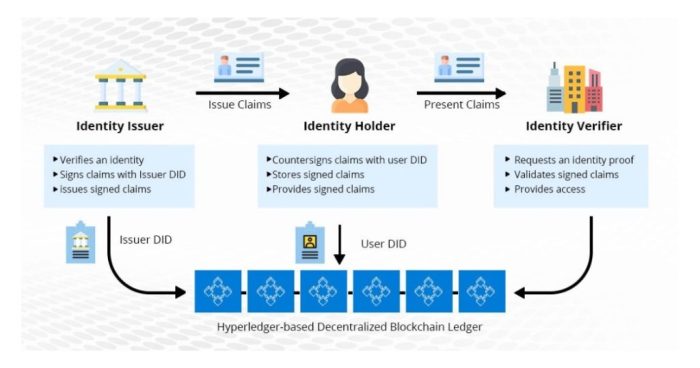
Implementing blockchain-based identity systems at a large scale presents significant scalability challenges. The inherent limitations of current blockchain architectures can hinder the adoption of this technology for widespread identity management. Understanding these limitations and exploring potential solutions is crucial for realizing the full potential of blockchain in this domain.
A key aspect of scalability involves the speed and efficiency of transaction processing. Traditional blockchains, especially those using Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, can struggle to handle the high volume of transactions required for a global identity system. This leads to increased latency and higher costs, making the system impractical for widespread use.
Consensus Mechanism Comparison, The potential use of blockchain technology in identity management.
Different consensus mechanisms significantly impact the performance and scalability of blockchain identity solutions. Proof-of-Work (PoW), while secure, is notoriously slow and energy-intensive, making it unsuitable for high-throughput identity systems. Proof-of-Stake (PoS) offers improved efficiency by rewarding validators based on their stake, leading to faster transaction processing. Other mechanisms like Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) offer further improvements in scalability but may compromise decentralization to varying degrees.
The choice of consensus mechanism depends on the specific requirements of the identity system, balancing security, speed, and decentralization.
Strategies for Improving Scalability and Performance
Several strategies can be employed to enhance the scalability and performance of blockchain-based identity systems. These include sharding, which partitions the blockchain into smaller, more manageable pieces, allowing for parallel processing of transactions. Layer-2 scaling solutions, such as state channels and sidechains, can also significantly improve transaction throughput by offloading some processing to off-chain mechanisms. Furthermore, optimizing data structures and improving the efficiency of smart contracts can contribute to faster transaction times and reduced resource consumption.
Finally, the use of more efficient consensus mechanisms and optimized hardware infrastructure can play a crucial role in enhancing performance.
Scaling Solutions Comparison
The following table compares different scaling solutions for blockchain, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages:
| Solution Name | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sharding | Partitions the blockchain into smaller, parallel shards. | Increased transaction throughput, improved scalability. | Increased complexity, potential for data inconsistency across shards. |
| State Channels | Allows transactions to occur off-chain, only settling the final state on-chain. | High throughput, low latency, reduced fees. | Requires participants to remain online, potential for disputes. |
| Rollups | Bundles multiple transactions into a single transaction and submits it to the main chain. | Improved scalability, reduced gas fees. | Increased complexity, potential for fraud if not implemented securely. |
| Sidechains | Separate blockchains that are pegged to the main chain. | Improved scalability, allows for experimentation with new features. | Security risks if not properly secured, potential for bridge attacks. |
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks: The Potential Use Of Blockchain Technology In Identity Management.

Navigating the legal landscape is crucial for the successful implementation of blockchain-based identity management systems. Existing regulations and emerging legal challenges significantly impact the design, deployment, and adoption of these technologies. Understanding these frameworks is essential for building trust and ensuring compliance.The integration of blockchain technology into identity management raises several legal and regulatory concerns. These stem from the decentralized nature of blockchain, the sensitive nature of personal data it handles, and the potential for misuse.
Addressing these issues proactively is key to fostering a secure and reliable environment for blockchain identity solutions.
Data Privacy Regulations and Blockchain Identity
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, and similar regulations worldwide, impose stringent requirements on the processing of personal data. These regulations mandate data minimization, purpose limitation, and the right to be forgotten. Implementing blockchain identity solutions requires careful consideration of these principles. For example, data stored on a blockchain is typically immutable, presenting a challenge to the “right to be forgotten.” Solutions involve techniques like data masking or using zero-knowledge proofs to verify identity without revealing sensitive information directly.
Careful architectural design is paramount to ensure compliance with data privacy regulations, potentially involving the use of private or permissioned blockchain networks to control data access and visibility.
Addressing Legal and Regulatory Concerns
Several approaches can mitigate legal and regulatory risks. These include developing robust data governance frameworks, implementing strong access control mechanisms, and engaging in proactive dialogue with regulatory bodies. Clear, transparent data handling policies are crucial, outlining how personal data is collected, stored, processed, and protected. Furthermore, working closely with legal experts to ensure compliance with all applicable laws and regulations is vital throughout the entire lifecycle of the blockchain identity system.
This collaboration should also include discussions on potential liabilities and risk mitigation strategies.
Potential Legal and Regulatory Hurdles
The widespread adoption of blockchain identity systems faces several significant legal and regulatory hurdles:
- Data ownership and control: Determining who owns and controls data stored on a blockchain, especially in decentralized systems, presents a significant challenge. This needs to be clearly defined to avoid conflicts and ensure compliance with existing data protection laws.
- Cross-border data transfer: The international nature of blockchain necessitates addressing cross-border data transfer regulations and ensuring compliance with diverse legal frameworks across jurisdictions.
- Data security and breach notification: Establishing clear protocols for data security and breach notification is vital to build trust and comply with data protection regulations. This includes defining responsibilities in case of breaches and establishing clear procedures for handling them.
- Compliance with existing identity verification regulations: Integrating blockchain identity systems with existing national identity verification systems and regulations may present significant challenges, requiring careful integration and interoperability solutions.
- Legal enforceability of smart contracts: The legal enforceability of smart contracts governing access and use of identity data on a blockchain needs clarification in many jurisdictions to provide legal certainty.
- Lack of standardized regulatory frameworks: The absence of clear, standardized global regulatory frameworks specifically for blockchain identity systems hinders wider adoption and creates uncertainty for businesses.
Ultimately, the application of blockchain technology to identity management holds immense potential for transforming how we interact with digital systems. While challenges remain in areas like scalability, standardization, and regulatory frameworks, the benefits in terms of security, privacy, and user control are undeniable. As blockchain technology matures and standards are established, we can anticipate a future where secure and user-centric digital identities become the norm, facilitated by the robust and transparent nature of blockchain.
Learn about more about the process of Analyzing the impact of technological advancements on the evolution of blockchain. in the field.
Check what professionals state about Exploring the use of blockchain technology in the art and entertainment industry. and its benefits for the industry.