The potential use of blockchain technology in healthcare. – The potential use of blockchain technology in healthcare is revolutionizing how we manage, share, and secure sensitive medical information. Imagine a world where patient records are instantly accessible to authorized providers, drug supply chains are completely transparent, and clinical trials run with unprecedented efficiency – all thanks to the secure and immutable nature of blockchain. This technology offers a powerful solution to many of healthcare’s biggest challenges, from data breaches to counterfeit medications.
This exploration delves into the various applications of blockchain in healthcare, examining its potential to improve data management, enhance interoperability, revolutionize supply chain management, streamline clinical trials, and even transform healthcare payments and insurance. We’ll discuss both the advantages and challenges associated with implementing this transformative technology, providing a comprehensive overview of its potential impact on the future of healthcare.
Data Management and Security in Healthcare using Blockchain: The Potential Use Of Blockchain Technology In Healthcare.
Blockchain technology offers a revolutionary approach to managing and securing sensitive patient health records. Its decentralized and immutable nature addresses many shortcomings of traditional systems, promising improved data integrity, enhanced privacy, and streamlined data sharing. This section explores how blockchain can transform healthcare data management.
Blockchain’s Enhanced Security and Privacy for Patient Health Records
Traditional healthcare systems often rely on centralized databases, making them vulnerable to data breaches and unauthorized access. Patient data is frequently stored in disparate systems, hindering interoperability and increasing the risk of security vulnerabilities. Blockchain, on the other hand, uses a distributed ledger, meaning patient data is replicated across multiple nodes in the network. This eliminates single points of failure and makes it significantly more difficult for malicious actors to compromise the entire system.
Furthermore, cryptographic techniques ensure data integrity and confidentiality. Access control mechanisms based on smart contracts allow granular control over who can view and modify specific patient data, enhancing privacy significantly. The immutability of the blockchain prevents unauthorized alterations to records, providing a verifiable audit trail for all data modifications. This contrasts sharply with traditional systems where data can be easily altered or deleted without detection.
System Architecture of a Blockchain-Based Healthcare System, The potential use of blockchain technology in healthcare.
The following table Artikels the key components and their functionalities within a hypothetical blockchain-based healthcare system:
| Component | Functionality | Data Interaction | Security Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient | Owns and controls their health data; grants access permissions. | Uploads data, views authorized records. | Uses strong authentication methods. |
| Healthcare Provider | Accesses and updates patient records with appropriate permissions; submits diagnoses and treatment plans. | Reads and writes data according to permissions. | Uses secure access credentials and encryption. |
| Blockchain Network | Stores and manages patient data securely and transparently; facilitates data sharing among authorized parties. | Receives, validates, and adds new blocks to the chain. | Utilizes cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms. |
| Smart Contracts | Enforces access control policies; automates data sharing protocols. | Triggers data release based on predefined rules. | Ensures data integrity and confidentiality. |
Scenario Illustrating Blockchain’s Improvement of Data Integrity and Prevention of Unauthorized Access
Imagine a patient, Alice, undergoing treatment at multiple hospitals. In a traditional system, her medical records might be scattered across different databases, potentially leading to inconsistencies and delays in care. In a blockchain-based system, Alice’s medical history is stored as a single, immutable record across the network. Each hospital involved has permission to access and update specific parts of her record, but all changes are cryptographically secured and recorded on the blockchain.
If a hospital attempts to alter Alice’s diagnosis without authorization, the blockchain will detect the discrepancy, preventing the fraudulent alteration and maintaining data integrity. Furthermore, Alice retains control over who can access her data, ensuring her privacy is protected.
Challenges of Implementing Blockchain for Data Management in a Large, Decentralized Healthcare Network
Implementing blockchain in a large, decentralized healthcare network presents several challenges. Interoperability between different blockchain platforms and legacy systems needs to be addressed. Scalability remains a concern, as handling the massive volume of healthcare data requires efficient and cost-effective solutions. Regulatory compliance and data governance are crucial considerations, ensuring adherence to privacy laws like HIPAA. The need for robust security measures and effective key management is paramount to prevent unauthorized access and maintain data integrity.
Finally, the lack of standardization and the need for widespread adoption among healthcare providers pose significant hurdles to overcome.
Improving Interoperability and Data Sharing with Blockchain
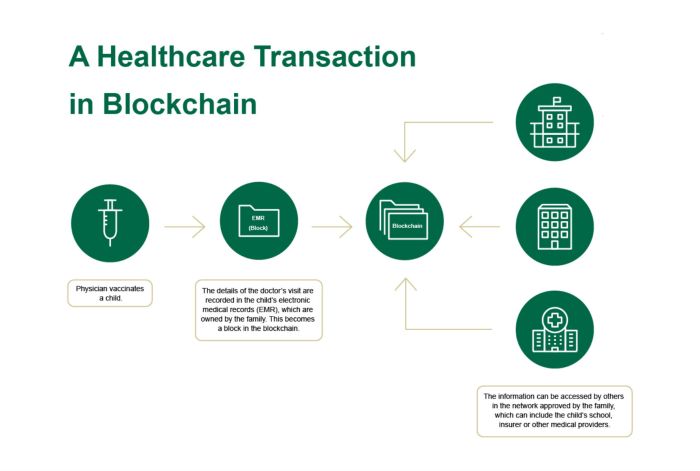
Blockchain technology offers a transformative approach to healthcare data management, particularly in addressing the persistent challenges of interoperability and secure data sharing. Its decentralized and immutable nature provides a robust framework for streamlining information exchange between disparate healthcare systems and providers, ultimately improving patient care. This section explores the potential of blockchain to revolutionize healthcare data sharing.
The current healthcare landscape is fragmented, with numerous independent systems and providers often lacking seamless communication. This results in duplicated efforts, data silos, and difficulties in providing holistic patient care. Blockchain’s distributed ledger technology offers a solution by creating a shared, secure, and transparent platform for data exchange. This allows authorized parties to access and share relevant patient information without compromising security or privacy.
Blockchain’s Role in Facilitating Seamless Data Exchange
Blockchain facilitates seamless data exchange by creating a shared, immutable record of patient data that can be accessed by authorized parties across different healthcare systems. Unlike traditional systems, which rely on centralized databases vulnerable to breaches and single points of failure, blockchain uses a decentralized network, enhancing security and resilience. Data is encrypted and stored across multiple nodes, making it incredibly difficult to alter or delete without detection.
This transparency and security build trust among participating entities, fostering collaboration and improving the overall efficiency of healthcare data sharing. The cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms ensure data integrity and authenticity.
Comparison of Blockchain and Health Information Exchanges (HIEs)
While Health Information Exchanges (HIEs) aim to improve interoperability, they often face challenges related to data security, standardization, and scalability. Blockchain offers several advantages over traditional HIEs. Blockchain’s decentralized nature eliminates single points of failure, making it more resilient to cyberattacks. Its cryptographic security features ensure data integrity and confidentiality, surpassing the security limitations of many HIEs.
Furthermore, blockchain’s inherent transparency and auditability enhance accountability and trust. However, blockchain implementation can be complex and expensive, requiring significant technical expertise and infrastructure investment. The lack of widespread standardization and interoperability between different blockchain platforms also presents a challenge. Existing HIEs benefit from established infrastructure and regulatory frameworks, while blockchain solutions are still evolving in this regard.
Notice What are the different types of consensus mechanisms used in blockchain technology? for recommendations and other broad suggestions.
Securely Sharing Patient Data Using a Blockchain-Based Platform
Securely sharing patient data using a blockchain-based platform involves a series of carefully orchestrated steps to ensure data integrity, confidentiality, and compliance with relevant regulations.
Investigate the pros of accepting Understanding the role of miners in maintaining the security of blockchain networks. in your business strategies.
The following procedure Artikels the process:
- Patient Consent and Authorization: The patient explicitly consents to the sharing of specific data with designated healthcare providers or systems.
- Data Encryption and Hashing: Patient data is encrypted using robust cryptographic techniques before being added to the blockchain. Hashing ensures data integrity, allowing detection of any unauthorized modifications.
- Data Entry and Validation: Authorized personnel enter the encrypted data onto the blockchain network. The data is validated by multiple nodes to prevent fraudulent entries.
- Access Control and Permissions: A sophisticated access control system manages who can access specific data elements. Permissions are defined based on roles and responsibilities.
- Data Retrieval and Decryption: Authorized parties can retrieve the encrypted data from the blockchain. Decryption is performed using secure keys to access the original information.
- Audit Trail and Transparency: Every transaction on the blockchain is recorded, creating an immutable audit trail that tracks data access, modifications, and sharing activities.
Examples of Successful Blockchain Implementations for Data Sharing
While widespread adoption is still underway, several promising examples demonstrate blockchain’s potential for improving healthcare data sharing. For instance, some hospitals are exploring blockchain for securely sharing medical images, allowing radiologists in different locations to access and analyze scans without compromising patient privacy. Other projects focus on sharing electronic health records (EHRs) across different healthcare providers, streamlining the process of patient care transitions.
While specific details of these implementations are often kept confidential due to data privacy concerns, the underlying principle remains the same: leveraging blockchain’s security and transparency to enhance data sharing.
Supply Chain Management and Drug Traceability
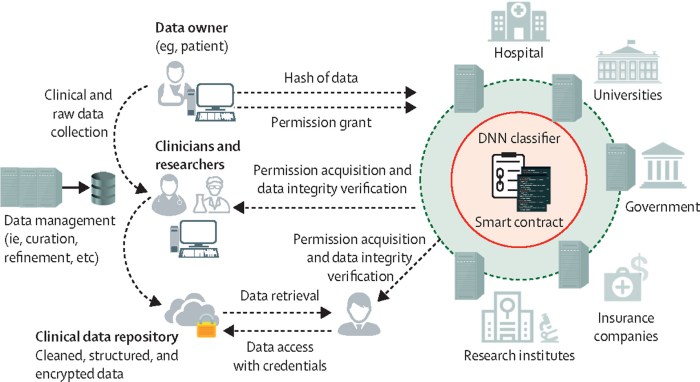
Blockchain technology offers a revolutionary approach to managing pharmaceutical supply chains, addressing long-standing challenges related to counterfeiting, diversion, and inefficient tracking. Its inherent security and transparency features make it uniquely suited to ensuring the authenticity and integrity of medications from manufacturer to patient.
A blockchain-based system for drug traceability leverages the immutable nature of blockchain to create a permanent, auditable record of a drug’s journey. This significantly reduces the risk of counterfeit drugs entering the market and improves overall supply chain efficiency.
Blockchain-Based Pharmaceutical Tracking System Design
A robust blockchain system for tracking pharmaceuticals would involve several key components. Each drug package would be assigned a unique identifier, perhaps a QR code or RFID tag, linked to a blockchain entry containing detailed information about its manufacturing, distribution, and handling. This information might include the manufacturer’s details, date of manufacture, batch number, expiry date, and a record of every transaction along the supply chain.
Access to this information would be controlled using cryptographic keys, ensuring data integrity and preventing unauthorized modifications. Smart contracts could automate various stages of the supply chain, such as triggering alerts when a package is delayed or reaches its expiry date. Regular audits and verification processes would maintain the system’s accuracy and reliability. Furthermore, incorporating tamper-evident packaging and blockchain-based authentication mechanisms would provide an extra layer of security.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Blockchain Implementation
The following table compares the costs and benefits of implementing a blockchain-based drug traceability system against traditional methods:
| Feature | Blockchain | Traditional Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Implementation Cost | High initial investment in infrastructure and software development; ongoing maintenance costs. | Lower initial cost, but potential for higher costs associated with manual tracking and investigation of counterfeits. |
| Data Security | High level of security due to cryptographic hashing and decentralized nature. | Vulnerable to data breaches and manipulation. |
| Traceability | Complete and transparent traceability throughout the supply chain. | Limited and often fragmented traceability. |
| Counterfeit Detection | Real-time detection of counterfeit drugs. | Detection often occurs after counterfeit drugs have entered the market. |
Scenario: Preventing Counterfeit Drug Distribution
Imagine a scenario where a pharmaceutical company uses a blockchain-based system to track its medication. Each package is uniquely identified and its journey is recorded on the blockchain. A pharmacy receives a shipment, scans the package’s unique identifier, and verifies its authenticity on the blockchain. The system flags a discrepancy: the batch number on the package doesn’t match the information on the blockchain, indicating a potential counterfeit.
This immediate alert prevents the counterfeit drugs from reaching patients, minimizing potential harm. The system also allows for immediate tracking of the source of the counterfeit product, leading to efficient investigation and prosecution of those involved in the fraud. This scenario highlights the significant potential of blockchain to enhance drug safety and public health.
Clinical Trials and Research using Blockchain

Blockchain technology offers a revolutionary approach to managing clinical trials, addressing long-standing challenges related to data security, transparency, and efficiency. Its decentralized and immutable nature creates a trustworthy environment for storing and sharing sensitive patient information, accelerating the research process and improving the overall quality of clinical trials.Blockchain can significantly improve the efficiency and transparency of clinical trials by providing a secure and auditable record of all trial activities.
This includes patient enrollment, data collection, analysis, and regulatory reporting. The inherent security features of blockchain minimize the risk of data breaches and tampering, ensuring the integrity of research findings. Furthermore, the transparency offered by blockchain allows all stakeholders – researchers, sponsors, patients, and regulators – to access relevant data, fostering trust and collaboration.
Patient Consent and Data Access Management
A blockchain-based system for managing patient consent and data access in clinical trials would operate by securely storing patient consent forms on the blockchain. Each consent would be uniquely identifiable and cryptographically secured, preventing unauthorized alteration or deletion. Patients would retain control over their data, granting or revoking access to specific researchers or institutions as needed. This system could utilize smart contracts to automate the process of data access, ensuring compliance with patient preferences and regulatory requirements.
For instance, a smart contract could be programmed to automatically release anonymized data to a research team upon successful verification of their credentials and the patient’s explicit consent. The entire process would be recorded on the blockchain, creating a transparent and auditable trail of data access.
Challenges in Using Blockchain for Clinical Trials
Implementing blockchain in clinical trials faces several challenges. Regulatory compliance is a major hurdle, as current regulations may not fully address the use of blockchain technology in healthcare. Data privacy is another critical concern, as blockchain, while secure, requires careful consideration of data anonymization and access control mechanisms to comply with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. The scalability of blockchain solutions for large-scale clinical trials needs to be addressed, as handling massive datasets can pose significant technical challenges.
Finally, the lack of widespread adoption and interoperability between different blockchain platforms could hinder the seamless exchange of data among researchers and institutions.
Facilitating Data Sharing and Collaboration
Blockchain facilitates data sharing and collaboration among researchers by creating a secure and transparent platform for data exchange. Researchers can access relevant data while maintaining patient privacy and data integrity. This shared platform eliminates data silos and enables efficient data aggregation and analysis, accelerating the pace of research. For example, researchers working on different aspects of a clinical trial can securely access and share relevant data subsets, without compromising the privacy of individual patients.
This collaborative environment can lead to faster identification of trends, improved outcomes, and more efficient development of new treatments.
Healthcare Payments and Insurance using Blockchain
Blockchain technology offers a compelling solution to the inefficiencies and high administrative costs plaguing the healthcare payments and insurance landscape. Its decentralized and secure nature can revolutionize how claims are processed, payments are made, and fraud is detected, ultimately benefiting both providers and patients. This section will explore the transformative potential of blockchain in streamlining healthcare finance.
The current healthcare payment system is often characterized by slow processing times, high administrative overhead, and a lack of transparency. Multiple intermediaries, complex paperwork, and manual reconciliation processes contribute to delays and increased costs. Blockchain’s inherent ability to create a shared, immutable ledger can significantly improve this situation. By automating processes and reducing the need for intermediaries, blockchain promises to drastically cut costs and improve efficiency.
Automated Insurance Claims Processing
Blockchain can automate the insurance claims process by creating a secure and transparent system where all stakeholders—patients, providers, and insurers—have access to the same information in real-time. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code, can be used to automatically verify the validity of claims based on predefined criteria, triggering payments upon verification.
This eliminates the need for manual review and significantly reduces processing times. For example, a smart contract could automatically release payment to a provider once a patient’s insurance coverage is verified and the claim details are confirmed accurate. This automated system reduces delays in reimbursements for providers and speeds up the process for patients.
Enhanced Transparency and Reduced Fraud
The immutable nature of blockchain enhances transparency throughout the claims processing workflow. All transactions are recorded on the blockchain, creating an auditable trail that can be accessed by all authorized parties. This transparency makes it easier to detect and prevent fraudulent activities. For instance, if a claim is flagged as potentially fraudulent, all parties can quickly review the transaction history to investigate and resolve the issue.
This improved transparency and traceability reduces the risk of fraud and builds trust among all stakeholders.
Conceptual Model: Smart Contracts for Automated Payments and Fraud Detection
Imagine a system where a patient’s medical record, including diagnosis and treatment details, is securely stored on a blockchain. A smart contract is then created that Artikels the payment terms between the insurer and the provider. Upon completion of treatment, the provider submits a claim to the blockchain. The smart contract automatically verifies the claim against the patient’s insurance policy and the medical records stored on the blockchain.
If everything aligns, the smart contract automatically releases payment to the provider. Simultaneously, the system can analyze patterns and anomalies within the claims data to identify potential fraudulent activities, flagging suspicious transactions for further investigation. This model minimizes manual intervention, reduces processing times, and enhances fraud detection capabilities.
Security Implications of Handling Sensitive Financial Data
While blockchain offers enhanced security features, it’s crucial to address the security implications of handling sensitive financial data within the healthcare ecosystem. Robust access control mechanisms are essential to ensure that only authorized parties can access and modify information. Data encryption techniques, both at rest and in transit, are critical to protecting patient privacy and financial information. Regular security audits and penetration testing are necessary to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, compliance with relevant data privacy regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States, is paramount to ensure responsible data handling and maintain patient trust.
Blockchain technology holds immense promise for transforming the healthcare industry. From enhancing data security and interoperability to improving supply chain transparency and streamlining clinical trials, its potential applications are vast and far-reaching. While challenges remain in terms of implementation and regulation, the potential benefits of increased efficiency, security, and trust make blockchain a compelling solution for many of healthcare’s most pressing issues.
As the technology matures and adoption increases, we can expect to see even more innovative applications emerge, ultimately leading to a more efficient, secure, and patient-centric healthcare system.