The impact of blockchain technology on the development of smart cities. – The impact of blockchain technology on the development of smart cities is transformative. Imagine a city where governance is transparent, data is secure, resources are managed efficiently, and citizens are actively engaged. This isn’t science fiction; blockchain technology offers the tools to build such a future. We’ll explore how this revolutionary technology is reshaping urban landscapes, enhancing citizen services, and driving economic growth.
From improving the accountability of municipal spending to creating secure digital identities for citizens, blockchain offers a myriad of solutions to the challenges faced by modern cities. We will delve into specific applications, examining how blockchain can optimize resource allocation, enhance data security, and foster greater citizen participation in city governance. The potential benefits are vast, ranging from reduced corruption to improved public services and increased economic efficiency.
Efficient Resource Management and Optimization in Smart Cities
Blockchain technology offers a powerful toolset for optimizing resource management in smart cities, enhancing efficiency, and minimizing waste. Its decentralized and transparent nature allows for better tracking, accountability, and automation of resource allocation, leading to significant improvements in sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
Blockchain’s impact on resource management stems from its ability to create immutable records of transactions and its facilitation of smart contracts. This allows for automated processes, increased transparency, and reduced reliance on centralized authorities, leading to more efficient and equitable resource distribution.
Blockchain Optimization of Energy, Water, and Waste Management
Blockchain can revolutionize how smart cities manage energy, water, and waste. For energy, imagine a system where each household’s energy consumption is recorded on a blockchain. This data could then be used to optimize energy distribution, incentivize energy conservation through rewards (like reduced energy bills), and even facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading within a microgrid. Similarly, water usage could be tracked and billed based on actual consumption, preventing leaks and promoting responsible water management.
Waste management could see improvements through tracking waste collection routes, optimizing pickup schedules, and even incentivizing recycling programs based on blockchain-verified participation. This granular level of data and automation significantly improves efficiency and reduces waste. For example, a city could use blockchain to identify areas with high energy consumption and target energy-saving initiatives accordingly.
Decentralized Energy Grids and Microgrids Enabled by Blockchain
Blockchain facilitates the creation of decentralized energy grids and microgrids by enabling secure and transparent peer-to-peer energy trading. This eliminates reliance on a single, centralized power source, making the grid more resilient and less vulnerable to outages.
Here’s a flowchart illustrating the process:
Flowchart: Decentralized Energy Trading via Blockchain
1. Energy Generation: A homeowner with solar panels generates excess energy.
Discover the crucial elements that make How to protect yourself from cryptocurrency scams and fraud. the top choice.
2. Energy Metering: Smart meters record energy generation and consumption.
3. Transaction Initiation: The homeowner initiates a transaction to sell excess energy to a neighbor via a blockchain-based platform.
4. Transaction Verification: The blockchain network verifies the transaction, ensuring its authenticity and accuracy.
5. Energy Transfer: The excess energy is transferred to the neighbor’s home.
For descriptions on additional topics like Comparing the transaction speeds of Solana, Ethereum, and Bitcoin blockchains., please visit the available Comparing the transaction speeds of Solana, Ethereum, and Bitcoin blockchains..
6. Payment Processing: Automated payment is processed via smart contract, based on the energy transferred and pre-agreed price.
7. Record Keeping: The entire transaction is recorded immutably on the blockchain.
Smart Contracts for Resource Allocation and Payment, The impact of blockchain technology on the development of smart cities.
Smart contracts automate resource allocation and payment, ensuring transparency and efficiency. These self-executing contracts are triggered automatically upon the fulfillment of pre-defined conditions.
Scenario: Smart Contract for Water Distribution
Imagine a smart city where water distribution is managed by a smart contract. Each household has a smart meter that records its water consumption. The smart contract automatically calculates the water bill based on consumption and sends a payment request to the household’s account. If payment is not received within a specified timeframe, the contract automatically restricts water supply until payment is made.
This system ensures fair billing, reduces water theft, and optimizes water resource management. The transparency offered by the blockchain also allows for audits and ensures accountability.
Enhanced Public Services and Citizen Engagement

Blockchain technology offers a transformative potential for enhancing public services and boosting citizen engagement in smart cities. Its inherent security, transparency, and immutability features create a fertile ground for innovative solutions that improve the efficiency and accessibility of government services while fostering a more participatory and inclusive urban environment. This section explores how blockchain can revolutionize healthcare, education, public safety, and citizen identity management, ultimately leading to a more responsive and citizen-centric smart city.
Blockchain’s decentralized nature and robust security mechanisms are ideal for streamlining the delivery of public services. By creating secure and transparent systems, blockchain can address many of the challenges associated with traditional, centralized systems, including data breaches, fraud, and inefficient processes.
Improved Public Service Delivery
Blockchain can significantly improve the delivery of public services across various sectors. In healthcare, blockchain can securely store and manage patient medical records, ensuring data privacy and interoperability between different healthcare providers. Imagine a system where patients have complete control over their medical data, granting access only to authorized personnel. This eliminates the risk of data loss or unauthorized access, leading to improved patient care and reduced administrative burdens.
In education, blockchain can securely manage academic credentials and certificates, preventing fraud and making verification simpler and faster. For example, a student’s transcript could be stored on a blockchain, verifiable by any institution globally, eliminating the need for cumbersome paper-based processes. In public safety, blockchain can enhance emergency response systems by providing real-time, tamper-proof records of incidents and facilitating information sharing between different agencies.
This can lead to quicker response times and improved coordination during emergencies.
Secure Digital Identity Management
Establishing a secure and efficient digital identity management system is crucial for a functioning smart city. Blockchain provides a robust foundation for such a system, offering several key benefits:
- Enhanced Privacy: Citizens have complete control over their data, deciding what information to share and with whom.
- Improved Security: Blockchain’s cryptographic security ensures data integrity and prevents unauthorized access or modification.
- Streamlined Verification: Verifying identities becomes significantly faster and more efficient, reducing bureaucratic hurdles.
- Interoperability: Different government agencies and private organizations can seamlessly share verified identity information.
- Reduced Fraud: The immutability of blockchain makes it nearly impossible to forge or tamper with identity documents.
Citizen Engagement and Blockchain-Based Reward System
Blockchain can significantly enhance citizen engagement by providing transparent and verifiable mechanisms for participation and rewarding contributions. A blockchain-based reward system can incentivize active participation in smart city initiatives.
Here’s a potential system design:
- Citizen Participation: Citizens can contribute to various smart city initiatives, such as reporting issues, providing feedback on city services, or participating in community projects. Their contributions are recorded on the blockchain.
- Contribution Verification: A decentralized system of validators (potentially including city officials and community members) verifies the authenticity and impact of citizen contributions.
- Reward Allocation: Based on the verified contributions, citizens earn tokens or points on the blockchain. These tokens could be exchanged for discounts on city services, access to exclusive events, or even direct monetary rewards.
- Transparency and Auditability: The entire reward system is transparent and auditable, ensuring fairness and preventing manipulation.
- Community Governance: The community could participate in governance decisions related to the reward system, ensuring the system evolves to meet their needs.
The Economic Impact of Blockchain in Smart City Development: The Impact Of Blockchain Technology On The Development Of Smart Cities.
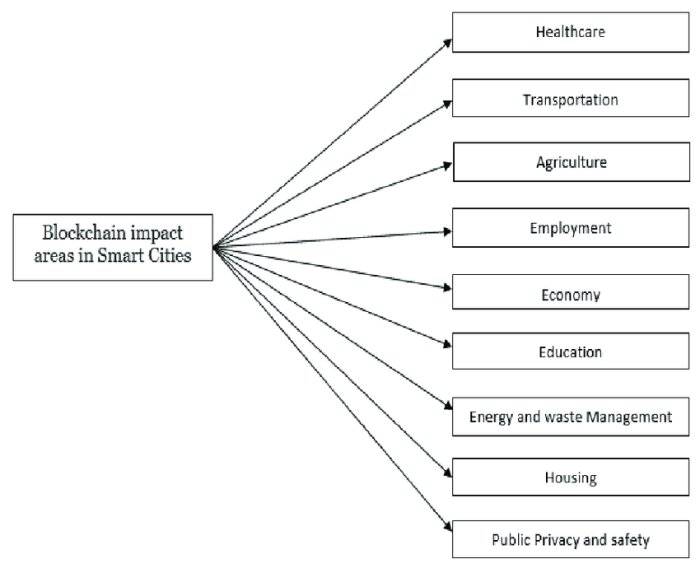
Blockchain technology presents a compelling opportunity to reshape the economic landscape of smart cities, promising significant cost savings, efficiency gains, and the creation of entirely new economic sectors. Its decentralized and transparent nature can foster trust, reduce fraud, and streamline processes across various city services, ultimately leading to a more robust and resilient economy.
Cost Savings and Efficiency Gains
Implementing blockchain can lead to substantial cost reductions for smart cities. For example, automating processes like land registration and permit issuance reduces administrative overhead, eliminates paperwork, and minimizes human error. The immutability of blockchain data also reduces the costs associated with verifying information and resolving disputes. Increased efficiency in resource allocation, facilitated by smart contracts and data transparency, further contributes to cost savings.
Imagine a city where streetlight maintenance is optimized through real-time data analysis on a blockchain, minimizing energy consumption and reducing repair costs. This efficiency extends to supply chain management, enabling more precise inventory control and reducing waste.
New Economic Opportunities
Blockchain’s transformative potential extends beyond cost savings to the creation of new economic opportunities. The development and implementation of blockchain-based solutions require specialized skills, leading to job creation in areas such as blockchain development, cybersecurity, and data analytics. Furthermore, the transparency and security offered by blockchain can attract new businesses and investments to the city, stimulating economic growth.
For example, a city could develop a blockchain-based platform for its local currency, encouraging local spending and boosting the local economy. The creation of new digital assets and services built on blockchain infrastructure also presents a lucrative avenue for entrepreneurship and innovation.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Blockchain Adoption
| Aspect | Costs | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Implementation | Initial investment in infrastructure, software, and training; potential disruption during transition. | Long-term cost savings through automation and efficiency gains; reduced fraud and corruption. |
| Maintenance | Ongoing maintenance and updates of blockchain systems; need for skilled personnel. | Reduced administrative costs; improved data security and reliability. |
| Security | Risk of cyberattacks and data breaches; need for robust security measures. | Enhanced security and transparency; reduced risk of fraud and data manipulation. |
| Scalability | Challenges in scaling blockchain systems to accommodate large amounts of data and transactions. | Improved efficiency in resource allocation; enhanced interoperability between different city systems. |
Challenges and Risks of Blockchain Adoption
While the economic benefits are substantial, the adoption of blockchain in smart cities also presents challenges. The initial investment in infrastructure and training can be significant, potentially straining city budgets. Furthermore, the lack of standardized protocols and interoperability issues between different blockchain platforms can hinder seamless integration. Regulatory uncertainty and the need for robust security measures to mitigate the risk of cyberattacks are also key concerns.
The complexity of blockchain technology requires a skilled workforce, which may necessitate investment in education and training programs.
Impact on Job Creation and Economic Growth
The adoption of blockchain technology can stimulate significant job creation and economic growth in smart cities. The demand for blockchain developers, cybersecurity experts, data analysts, and other related professionals will increase. Furthermore, the development of blockchain-based applications and services will create new businesses and entrepreneurial opportunities, leading to the expansion of the local economy. For instance, a city could develop a blockchain-based platform for managing its public transportation system, creating jobs in software development, system maintenance, and customer support.
The increased efficiency and transparency facilitated by blockchain can attract foreign investment and promote innovation, further boosting economic growth. A successful blockchain implementation can transform a city into a global hub for innovation and technology, attracting talent and investment from around the world.
In conclusion, the integration of blockchain technology into smart city development holds immense promise. By enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency across various city functions, blockchain empowers cities to become more responsive, resilient, and citizen-centric. While challenges remain, the potential rewards – from improved governance to enhanced public services and economic growth – make the exploration and implementation of blockchain solutions a crucial step towards building truly smart and sustainable cities for the future.
The journey towards a more efficient and equitable urban landscape is paved with the innovative possibilities offered by blockchain.