Is ZetaChain a good investment for long-term growth? That’s a question many crypto investors are asking. ZetaChain aims to revolutionize cross-chain interoperability, promising seamless communication between different blockchains. But is this innovative technology a sound long-term investment? We’ll dive into the tech, market analysis, tokenomics, and risk assessment to help you decide.
This exploration will cover ZetaChain’s unique features, its competitive landscape, and the potential for growth within the burgeoning cross-chain market. We’ll analyze the token’s value drivers, assess potential risks, and explore various scenarios to give you a comprehensive overview.
ZetaChain’s Technology and Innovation

ZetaChain aims to revolutionize blockchain interoperability with its novel approach to cross-chain communication. Unlike many competitors relying on bridges or sidechains, ZetaChain employs a unique architecture designed for enhanced security, scalability, and functionality. This approach offers significant potential advantages in a rapidly evolving blockchain landscape.ZetaChain’s Cross-Chain Interoperability and AdvantagesZetaChain’s core innovation lies in its omnichain architecture. Instead of relying on separate bridges for each blockchain, ZetaChain creates a single, unified network that allows for seamless communication and asset transfer between multiple blockchains.
This eliminates the vulnerabilities often associated with individual bridges, which can be targets for hacks and exploits. The unified network also allows for increased speed and efficiency in cross-chain transactions. Competitors often struggle with latency and high transaction fees when bridging assets between chains; ZetaChain’s architecture is designed to mitigate these issues. Furthermore, ZetaChain’s approach allows for the creation of truly decentralized applications (dApps) that can interact with various blockchains without being confined to a single ecosystem.
This fosters innovation and allows developers to tap into the strengths of multiple chains simultaneously.ZetaChain’s Architecture: Scalability and Security FeaturesZetaChain’s architecture incorporates several key features that contribute to its scalability and security. The system utilizes a novel consensus mechanism, combining elements of proof-of-stake and a Byzantine fault-tolerant consensus algorithm to ensure both security and efficient transaction processing. This hybrid approach aims to provide a higher level of security compared to systems relying solely on proof-of-stake, while maintaining a relatively high throughput.
The modular design of ZetaChain’s architecture also allows for easy upgrades and integration of new blockchains as needed. This adaptability is crucial in a dynamic market where new blockchains are constantly emerging. Security is further enhanced through advanced cryptographic techniques and rigorous auditing processes.Comparison with Other Blockchain ProjectsSeveral other projects are working on interoperability solutions, but ZetaChain’s approach differs significantly.
Cosmos, for example, uses a network of interconnected blockchains (zones) that communicate through the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol. While IBC provides interoperability, it can be complex to set up and manage. Polkadot employs a relay chain that connects various parachains, each with its own functionality. However, parachain slots are limited and highly competitive. LayerZero, a popular bridging solution, offers a more centralized approach than ZetaChain’s omnichain architecture, potentially posing greater security risks.
The key difference is ZetaChain’s attempt to create a truly decentralized, unified network, minimizing reliance on centralized components and single points of failure.Technological Challenges and Potential SolutionsWhile ZetaChain’s technology holds promise, it also faces challenges. One significant challenge is maintaining the security and scalability of the omnichain network as it integrates more blockchains. The complexity of managing a vast network of different consensus mechanisms and data structures requires robust engineering solutions.
Another challenge lies in ensuring compatibility with a wide range of blockchain protocols, each with its unique specifications and requirements. ZetaChain addresses these challenges through ongoing research and development, focusing on enhancing its consensus mechanism, improving its modular architecture, and developing robust compatibility layers. The team also emphasizes community involvement and rigorous security audits to mitigate risks.Technical Specifications Comparison
| Feature | ZetaChain | Cosmos | Polkadot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interoperability Approach | Omnichain | IBC Protocol | Relay Chain & Parachains |
| Consensus Mechanism | Hybrid (PoS & BFT) | Tendermint | Nominated Proof-of-Stake |
| Scalability | High (claimed) | Moderate to High (depending on zone) | Moderate (limited parachain slots) |
| Security | High (claimed, subject to audit) | Moderate to High | Moderate to High |
Market Analysis and Competition

The cross-chain interoperability market is rapidly evolving, presenting both significant opportunities and challenges for projects like ZetaChain. Understanding the competitive landscape and ZetaChain’s positioning within it is crucial for assessing its long-term investment potential. This section will analyze the key players, market size projections, and ZetaChain’s competitive advantages and disadvantages.The cross-chain interoperability space is crowded, with various projects offering different approaches to bridging blockchains.
Key players include established protocols like Cosmos, Polkadot, and Avalanche, each with a substantial market presence and established developer communities. These protocols have already captured significant market share, especially within their respective ecosystems. Newer entrants, like LayerZero and Conflux, are also vying for a piece of the pie, introducing innovative solutions and attracting attention. Precise market share figures are difficult to obtain due to the decentralized nature of the space and the lack of a centralized data repository.
However, it’s safe to say that the market is fragmented, with no single dominant player.
Market Size and ZetaChain’s Position
Estimating the precise market size for cross-chain solutions is challenging, but the potential is enormous. As the crypto ecosystem matures and more decentralized applications (dApps) require seamless interaction across different blockchains, the demand for interoperability solutions will likely increase exponentially. Analysts predict substantial growth in this market over the next few years, with projections varying depending on the adoption rate of decentralized finance (DeFi) and other blockchain-based applications.
ZetaChain aims to carve a niche within this expanding market by offering its unique omnichain capabilities. Its ability to execute smart contracts across multiple chains simultaneously could give it a competitive edge, potentially attracting developers seeking solutions for complex, multi-chain applications.
Competitive Landscape and ZetaChain’s Strengths and Weaknesses
ZetaChain’s main strengths lie in its novel omnichain architecture. Unlike other solutions that rely on bridges or relays, ZetaChain aims to provide a unified execution environment, enabling seamless communication and execution across different blockchains. This has the potential to solve several limitations of existing cross-chain technologies, such as scalability and security concerns related to bridge vulnerabilities. However, ZetaChain also faces challenges.
Its relatively new entry into the market means it lacks the established network effects and developer community of more mature projects. Furthermore, the complexity of its technology could present barriers to adoption, and the success of its omnichain approach remains to be fully proven.
Market Growth Scenarios and ZetaChain’s Market Share Capture
Several scenarios are possible for the future growth of the cross-chain interoperability market. A bullish scenario involves widespread adoption of DeFi and other multi-chain applications, leading to a rapidly expanding market with significant demand for solutions like ZetaChain’s. In this scenario, ZetaChain’s unique capabilities could allow it to capture a substantial market share, particularly among developers seeking advanced functionalities.
A more conservative scenario involves slower adoption rates and increased competition, resulting in a more fragmented market with several competing solutions. In this case, ZetaChain’s success would depend on its ability to establish itself as a leading player and differentiate itself from its competitors through innovation and strategic partnerships.
Potential Risks and Opportunities for ZetaChain’s Market Penetration
- Opportunity: Growing demand for cross-chain solutions driven by DeFi and metaverse development.
- Opportunity: Successful implementation of the omnichain architecture and demonstration of its superior capabilities.
- Opportunity: Strategic partnerships with major players in the blockchain ecosystem.
- Risk: Competition from established players with significant network effects and developer communities.
- Risk: Technological challenges in implementing and scaling the omnichain architecture.
- Risk: Security vulnerabilities and potential exploits, especially considering the complexity of the technology.
- Risk: Regulatory uncertainty and potential changes in the regulatory landscape impacting the cryptocurrency market.
Tokenomics and Investment Potential

Understanding ZetaChain’s tokenomics is crucial for assessing its long-term investment potential. The success of any blockchain project hinges not only on its technology but also on the design and execution of its economic model. This section delves into the key aspects of ZetaChain’s tokenomics, examining its potential for growth and comparing it to other successful projects.
ZetaChain Token Utility and Distribution
The ZetaChain token (ZETA) serves several key functions within the ecosystem. It’s used for staking to secure the network, paying transaction fees, and participating in governance decisions. The distribution of ZETA is designed to incentivize participation and ensure a balanced ecosystem. A significant portion is allocated to the community, encouraging long-term growth and engagement. The precise allocation percentages are subject to change based on the project’s roadmap and community needs, but a snapshot of the initial distribution is provided below.
This illustrates the intended balance between team, ecosystem development, and community involvement.
| Stakeholder | Allocation (%) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Ecosystem Fund | 30 | Funding development, grants, and marketing initiatives. |
| Team & Advisors | 15 | Compensation for core development team and advisors. |
| Private Sale | 25 | Early investors who contributed to the project’s initial development. |
| Public Sale & Airdrops | 30 | Community participation and distribution through various mechanisms. |
ZetaChain Inflation Model
ZetaChain’s inflation model is designed to balance the need for rewarding network participants with the goal of maintaining long-term token value. The specifics of the inflation rate and its adjustment mechanisms are crucial. A well-designed inflation model can ensure the long-term health of the ecosystem by incentivizing participation and mitigating the risk of deflation. A high inflation rate could dilute the value of existing tokens, while a low rate might not provide sufficient incentives for network participation.
A dynamic inflation model, adjusting based on network activity and other factors, could be a more sustainable approach. For comparison, consider projects like Cosmos, which employs a similar approach to incentivize validators and maintain network security.
Factors Influencing ZetaChain’s Long-Term Value
Several factors will influence the long-term value of the ZETA token. These include the adoption of ZetaChain’s cross-chain interoperability technology, the growth of the overall DeFi market, the network’s security and stability, and the effectiveness of its governance model. The successful integration of new features and the expansion of its developer community will also play a significant role.
Similar to how Ethereum’s value has increased with the growth of its DeFi ecosystem, ZetaChain’s success hinges on building a thriving and vibrant community around its technology.
Scenario Analysis of ZetaChain’s Token Price
Predicting the future price of any cryptocurrency is inherently speculative. However, we can explore potential scenarios based on different levels of adoption and market conditions. A bullish scenario might see widespread adoption of ZetaChain’s technology, leading to significant demand for ZETA and a substantial increase in its price. This could be comparable to the growth seen in other successful blockchain projects, such as Solana’s early growth phase.
A bearish scenario, on the other hand, might involve slower-than-expected adoption, leading to lower demand and a relatively stagnant or even declining price. A realistic scenario likely lies somewhere between these extremes, with moderate adoption and price appreciation. This would be similar to the growth pattern observed in many established cryptocurrencies that have shown sustained, though not explosive, growth over time.
Comparison with Other Successful Blockchain Projects
Comparing ZetaChain’s tokenomics to those of other successful blockchain projects like Cosmos, Polkadot, or Avalanche is crucial. Analyzing their token distribution models, inflation mechanisms, and governance structures provides valuable insights. The key areas of comparison should include token utility, distribution strategy, and the long-term sustainability of their economic models. This comparative analysis helps assess the strengths and weaknesses of ZetaChain’s approach and predict its potential for success.
For example, the success of Cosmos’ ATOM token, driven by its strong community and interoperability features, can serve as a benchmark for evaluating ZetaChain’s potential.
Adoption and Ecosystem Development
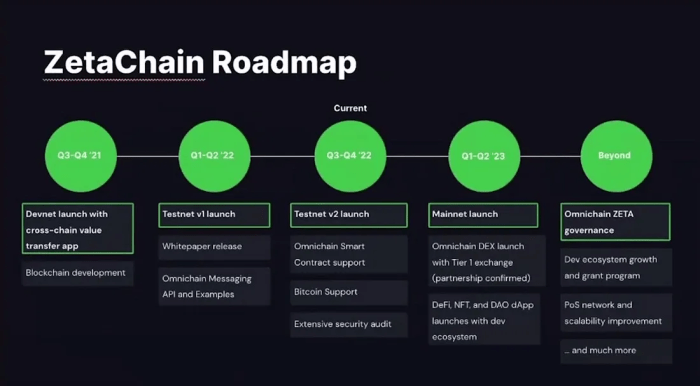
ZetaChain’s success hinges on widespread adoption and a thriving ecosystem. This requires strategic partnerships, a compelling developer experience, and a robust suite of applications built on the platform. The speed and scale of ecosystem growth will significantly impact ZetaChain’s long-term value proposition.Key Partnerships and Integrations are Crucial for Adoption. Strategic collaborations with prominent players in the DeFi and blockchain space are essential for increasing ZetaChain’s visibility and attracting users.
These partnerships can range from integrations with major exchanges and wallets to collaborations with established decentralized applications (dApps). Strong partnerships lend credibility and expand the network effect, accelerating user growth.
Current State and Future Growth Potential of the ZetaChain Ecosystem
Currently, the ZetaChain ecosystem is in its early stages of development. The platform’s unique interoperability features present a significant opportunity for innovation. The potential for future growth is substantial, particularly if ZetaChain successfully attracts developers and fosters the creation of a diverse range of dApps. This could lead to increased network activity, higher transaction volume, and ultimately, a more valuable token.
The success of similar projects like Cosmos, with its interconnected network of blockchains, demonstrates the potential for a thriving multi-chain ecosystem. Cosmos’ success stems from its robust tooling and a strong community of developers, factors ZetaChain needs to emulate and surpass to achieve its goals.
Factors Accelerating or Hindering Ecosystem Development
Several factors could significantly impact ZetaChain’s ecosystem development. Positive factors include the availability of developer-friendly tools and resources, a strong community, and successful marketing and outreach initiatives. Conversely, challenges include competition from other interoperability solutions, regulatory uncertainty, and the inherent risks associated with developing and deploying decentralized applications. The success of projects like Polkadot, with its parachain architecture allowing for independent blockchain development, serves as a benchmark for ZetaChain’s growth trajectory.
Polkadot’s robust ecosystem highlights the importance of a well-defined architecture and developer support in fostering innovation. However, Polkadot’s experience with parachain auctions and their complexities also serves as a cautionary tale; ZetaChain needs to design a smoother, more accessible onboarding process for developers.
Examples of Successful Blockchain Ecosystems and Comparisons to ZetaChain
Successful blockchain ecosystems, such as Ethereum and Solana, demonstrate the importance of a strong developer community and a wide range of applications. Ethereum’s dominance in the DeFi space highlights the power of network effects and the ability to attract and retain talented developers. Solana’s success in achieving high transaction speeds showcases the importance of technological innovation and efficiency.
ZetaChain’s potential lies in its unique approach to interoperability, which could offer advantages over existing solutions. However, it needs to demonstrate its ability to attract developers and build a compelling ecosystem to compete effectively with established players. The success of Cosmos’ IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication) protocol highlights the importance of seamless interoperability in fostering ecosystem growth. This is a crucial area where ZetaChain needs to excel to gain traction.
Potential Impact of Developer Adoption on ZetaChain’s Long-Term Success
Developer adoption is paramount to ZetaChain’s long-term success. A vibrant developer community is essential for creating new and innovative dApps that leverage ZetaChain’s unique features. The more developers build on ZetaChain, the more robust and valuable the ecosystem becomes. This, in turn, increases the demand for the ZETA token, leading to potential price appreciation and greater network security.
The rapid growth of the Ethereum ecosystem, fueled by a massive influx of developers, demonstrates the direct correlation between developer adoption and the overall success of a blockchain platform. ZetaChain needs to focus on attracting and supporting developers through initiatives such as grants, hackathons, and developer-friendly documentation to replicate this success.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies: Is ZetaChain A Good Investment For Long-term Growth?
Investing in any cryptocurrency, especially a relatively new project like ZetaChain, carries inherent risks. Understanding these risks and the strategies employed to mitigate them is crucial for making informed investment decisions. This section will explore the potential pitfalls of ZetaChain investment and examine the project’s approach to risk management.ZetaChain faces several key risk categories: technological, regulatory, and market risks.
Technological risks encompass the possibility of bugs, exploits, or unforeseen limitations in its novel cross-chain technology. Regulatory uncertainty regarding the classification and legal treatment of ZetaChain and its ZETA token presents a significant challenge. Finally, market risks involve the volatility of the cryptocurrency market itself, potential competition from other projects, and the overall adoption rate of ZetaChain’s technology.
Technological Risks and Mitigation
ZetaChain’s ambitious goal of seamless interoperability across multiple blockchains introduces complex technological challenges. Potential risks include vulnerabilities in the smart contract code, scalability issues as usage increases, and unforeseen interactions with different blockchain environments. ZetaChain aims to mitigate these risks through rigorous code audits by independent security firms, ongoing testing and development to improve scalability and stability, and a robust bug bounty program to incentivize the identification and resolution of vulnerabilities.
They are also emphasizing a modular design, allowing for easier upgrades and fixes without disrupting the entire system. A failure to effectively address these technological risks could lead to security breaches, service disruptions, and a loss of user trust, impacting the value of the ZETA token.
Regulatory Risks and Mitigation
The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies is constantly evolving and varies significantly across jurisdictions. Uncertainty surrounding the regulatory classification of ZetaChain and its token could lead to legal challenges, limitations on its use, or even outright bans in certain regions. ZetaChain’s strategy for mitigating this risk involves engaging with regulators globally, aiming for clarity and compliance with evolving rules.
They are proactively seeking to understand and adapt to the regulatory environment, aiming for a collaborative approach rather than confrontation. Adverse regulatory actions could severely restrict ZetaChain’s operations and negatively impact the value of its token.
Market Risks and Mitigation
Market risks are inherent to any cryptocurrency investment. These include the overall volatility of the cryptocurrency market, competition from other interoperability solutions, and the potential for slow adoption of ZetaChain’s technology. ZetaChain is attempting to mitigate these risks by focusing on building a strong and active ecosystem through partnerships, developer grants, and community engagement. They aim to demonstrate the practical utility of their technology and attract developers and users, creating network effects that bolster the value of the ZETA token.
However, even with these strategies, a bear market or the emergence of a superior competing technology could significantly depress the price of ZETA.
Comparison to Other Blockchain Projects
Compared to established projects, ZetaChain presents a higher risk profile due to its relative novelty and the complexity of its technology. Projects like Cosmos or Polkadot have already established themselves in the interoperability space, boasting larger communities and more mature ecosystems. However, ZetaChain’s unique approach to cross-chain communication might offer a competitive advantage if it can successfully overcome its technological and regulatory hurdles.
The risk profile is similar to other innovative, early-stage blockchain projects aiming to solve complex problems, which often involve higher risk and potentially higher reward.
Negative Outcome Scenarios and Impact, Is ZetaChain a good investment for long-term growth?
A severe security breach, leading to a significant loss of funds, would drastically impact the value of ZETA. Similarly, unfavorable regulatory actions, such as a complete ban in major markets, could cripple the project and lead to a near-total loss of investment. Slow adoption, coupled with increased competition, could render ZetaChain’s technology irrelevant, resulting in a decline in ZETA’s value.
These scenarios highlight the importance of careful risk assessment before investing.
Risk Mitigation Strategies for Investors
- Diversify your investment portfolio: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Allocate only a small percentage of your investment capital to ZetaChain.
- Stay informed: Keep up-to-date on ZetaChain’s development, regulatory updates, and market trends. Regularly review your investment and adjust accordingly.
- Thoroughly research: Understand the technology, team, and competitive landscape before investing. Read white papers, audit reports, and community discussions.
- Manage your expectations: Cryptocurrency investments are inherently volatile. Be prepared for potential losses and don’t invest more than you can afford to lose.
- Set stop-loss orders: Protect your investment by setting stop-loss orders to automatically sell your ZETA if the price falls below a predetermined level.
Ultimately, whether ZetaChain is a good long-term investment depends on your risk tolerance and investment strategy. While its innovative technology and potential market share are promising, the crypto market remains volatile and inherently risky. Thoroughly researching the project, understanding its limitations, and diversifying your portfolio are crucial steps before making any investment decision. The information provided here should serve as a starting point for your own due diligence.