How to diversify your cryptocurrency portfolio effectively. This isn’t just about throwing money at different coins; it’s about building a robust investment strategy that aligns with your risk tolerance and financial goals. We’ll explore various asset allocation models, from the classic 60/40 approach to more sophisticated strategies, and look at how to select cryptocurrencies based on market capitalization and potential.
We’ll also discuss the importance of diversifying
-beyond* crypto into traditional assets like stocks and bonds, and how to manage the risks inherent in this volatile market.
Understanding your risk tolerance is key. Are you a seasoned investor comfortable with high-risk, high-reward opportunities, or do you prefer a more conservative approach? Your answer will significantly influence how you structure your portfolio. We’ll cover different investor profiles and tailor diversification strategies to each, helping you create a plan that’s right for you. From choosing between Bitcoin, altcoins, stablecoins, and DeFi tokens to understanding market capitalization and the importance of rebalancing, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the crypto landscape effectively.
Understanding Risk Tolerance and Investment Goals

Diversifying your cryptocurrency portfolio isn’t just about spreading your investments across different coins; it’s deeply intertwined with your personal risk tolerance and investment objectives. Understanding these factors is crucial for building a portfolio that aligns with your comfort level and financial aspirations. Ignoring this crucial step can lead to unnecessary stress and potentially significant losses.Your risk tolerance directly impacts how you diversify.
A higher risk tolerance allows for a portfolio with a greater proportion of volatile, high-growth potential cryptocurrencies. Conversely, a lower risk tolerance necessitates a more conservative approach, favoring established, less volatile assets and potentially including more stablecoins or fiat currency. This relationship ensures your investment strategy reflects your personal comfort level with potential losses.
Defining Personal Investment Goals
Before diving into specific diversification strategies, it’s vital to clearly define your investment goals. What are you hoping to achieve with your cryptocurrency investments? Are you aiming for long-term growth, short-term gains, or a balance of both? Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals provides a framework for evaluating your portfolio’s performance and making informed adjustments. For example, aiming to accumulate a specific amount of Bitcoin within five years is a SMART goal, whereas simply “getting rich” is not.
Investor Profiles and Diversification Strategies
Different investor profiles necessitate distinct diversification strategies.
Consider three archetypal investors:
- The Conservative Investor: This investor prioritizes capital preservation over high returns. Their portfolio would likely consist of a significant percentage of stablecoins (like USDT or USDC), a smaller allocation to established, large-market-cap cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, and potentially some exposure to established, less volatile altcoins with a proven track record. They might also allocate a portion to traditional assets like bonds or stocks for further risk mitigation.
- The Moderate Investor: This investor seeks a balance between risk and reward. Their portfolio might include a mix of established cryptocurrencies, a selection of promising altcoins with moderate volatility, and potentially a small allocation to more speculative assets. They are comfortable with some price fluctuations but prioritize long-term growth over short-term gains. Their diversification strategy involves spreading investments across various asset classes to mitigate risk while still aiming for substantial returns.
- The Aggressive Investor: This investor is comfortable with high risk in pursuit of substantial returns. Their portfolio would likely include a larger percentage of altcoins, newer projects, and potentially even meme coins. They are willing to accept significant price volatility in exchange for the potential for higher growth. However, this approach necessitates a thorough understanding of the market and a higher tolerance for potential losses.
A well-informed strategy is paramount here.
It’s important to remember that these are just examples, and your ideal diversification strategy will depend on your unique circumstances and risk tolerance.
Asset Allocation Strategies: How To Diversify Your Cryptocurrency Portfolio Effectively.
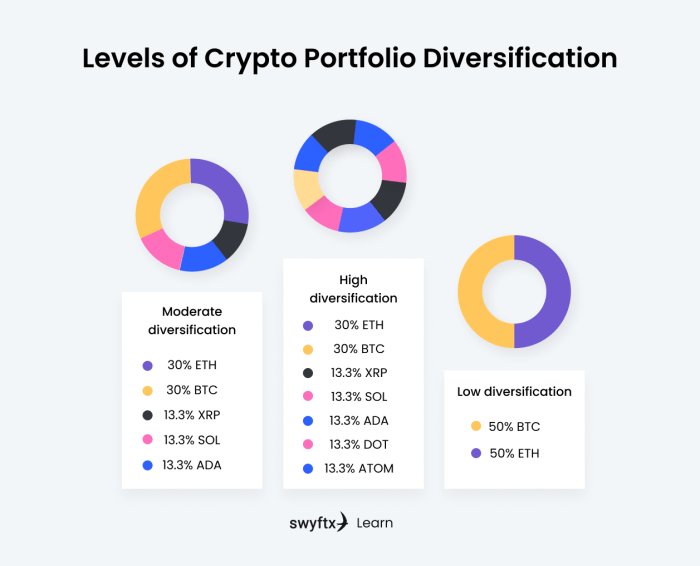
Diversifying your crypto portfolio isn’t just about owning many different coins; it’s about strategically allocating your funds across various asset classes to manage risk and potentially maximize returns. This involves understanding different asset allocation models and how they apply to the unique characteristics of the cryptocurrency market. We’ll explore some common models and how to tailor them to your risk tolerance.Asset allocation models help you decide how much of your portfolio to dedicate to each asset class.
They are frameworks, not rigid rules, and require adjustments based on market conditions and your individual circumstances. Consider them starting points for building a well-diversified portfolio, not the final answer.
Common Asset Allocation Models in Cryptocurrency
Several established models, typically used in traditional finance, can be adapted for cryptocurrency investing. However, remember that the cryptocurrency market is significantly more volatile than traditional markets, requiring a more cautious approach.
- 60/40 Portfolio: A classic model allocating 60% to growth assets (like Bitcoin and high-potential altcoins) and 40% to more stable assets (like stablecoins or less volatile altcoins). This provides a balance between potential high returns and risk mitigation.
- Risk Parity: This model aims for equal risk contribution from each asset class. This means that while you might have a larger allocation in less volatile assets, the overall risk contribution from each asset class remains similar. This requires sophisticated risk modeling, usually best left to advanced investors with specialized tools.
- Custom Allocation: Many investors prefer a custom allocation based on their individual risk tolerance and market outlook. This could involve a higher percentage in high-growth assets for aggressive investors or a more conservative approach with a higher percentage in stablecoins for risk-averse investors.
Allocating to Different Cryptocurrency Classes
The cryptocurrency market offers a wide range of asset classes, each with its own risk-return profile. Careful consideration of these differences is crucial for effective diversification.
- Bitcoin (BTC): Often considered the “safe haven” of cryptocurrencies due to its market dominance and established track record. A core holding in many portfolios, providing stability relative to other altcoins.
- Altcoins: A broad category encompassing all cryptocurrencies other than Bitcoin. This group exhibits high volatility and offers both significant potential returns and substantial risks. Diversification within altcoins themselves is vital, avoiding over-exposure to any single project.
- Stablecoins: Designed to maintain a stable value, typically pegged to a fiat currency like the US dollar. They offer a low-risk, low-return option for preserving capital and reducing portfolio volatility. However, it’s crucial to choose reputable and well-audited stablecoins.
- DeFi Tokens: Tokens representing ownership or participation in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. This sector offers high growth potential but also carries substantial risks due to the nascent nature of the technology and the potential for smart contract vulnerabilities.
Sample Asset Allocation Table
The following table illustrates different diversification strategies for various risk profiles. Remember, these are examples and should be adapted to your personal circumstances and risk tolerance. Always conduct thorough research before making any investment decisions.
| Risk Profile | Bitcoin (BTC) | Altcoins | Stablecoins | DeFi Tokens |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conservative | 40% | 10% | 50% | 0% |
| Moderate | 30% | 30% | 30% | 10% |
| Aggressive | 20% | 60% | 10% | 10% |
Market Capitalization and Cryptocurrency Selection

Market capitalization, the total value of a cryptocurrency’s circulating supply, is a crucial factor in diversifying your portfolio. Understanding a coin’s market cap helps assess its relative size, stability, and potential for growth. Larger market caps generally indicate greater liquidity and lower volatility, while smaller caps might offer higher growth potential but with increased risk. Diversifying across different market cap categories helps balance risk and reward.Choosing cryptocurrencies based solely on market cap isn’t sufficient; thorough research into the project’s fundamentals, team, and technology is also necessary.
However, market cap provides a useful initial filter for identifying potentially suitable assets for your portfolio.
Large-Cap Cryptocurrencies: Risks and Rewards
Large-cap cryptocurrencies, generally with market caps exceeding several billion dollars, tend to be more established and less volatile than their smaller counterparts. However, even these established projects carry inherent risks.
- Bitcoin (BTC): The original cryptocurrency, Bitcoin boasts high liquidity and widespread adoption. Risks: Regulatory uncertainty and potential competition from newer technologies. Rewards: Store of value potential, established network effect, and relatively stable price compared to smaller cryptocurrencies.
- Ethereum (ETH): The leading smart contract platform, Ethereum supports a vast ecosystem of decentralized applications (dApps) and NFTs. Risks: Network congestion and scalability challenges, competition from other layer-1 blockchains. Rewards: Exposure to the booming DeFi and NFT sectors, high potential for long-term growth.
- Tether (USDT): A stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, Tether aims to maintain a 1:1 ratio. Risks: Concerns about its reserves and regulatory scrutiny. Rewards: Provides a relatively stable asset within a volatile market, useful for hedging against crypto market downturns.
- Binance Coin (BNB): The native token of the Binance exchange, BNB offers utility within the Binance ecosystem. Risks: Centralized nature tied to Binance’s operations, regulatory risks affecting exchanges. Rewards: Access to Binance’s services and potential benefits from its growth.
- Solana (SOL): A high-performance blockchain known for its speed and scalability. Risks: Network outages in the past, centralized aspects of its validator network. Rewards: Potential for high growth due to its fast transaction speeds and vibrant ecosystem.
Mid-Cap and Small-Cap Cryptocurrencies
Mid-cap and small-cap cryptocurrencies represent a higher-risk, higher-reward segment of the market. Their smaller market caps mean greater price volatility but also potentially higher returns if the project succeeds. Remember to conduct thorough due diligence before investing in these assets.
Mid-Cap Cryptocurrencies (Market cap generally between $1 billion and $10 billion):
- Cardano (ADA)
- Polkadot (DOT)
- Avalanche (AVAX)
- Chainlink (LINK)
- Cosmos (ATOM)
Small-Cap Cryptocurrencies (Market cap generally below $1 billion):
- Algorand (ALGO)
- Near Protocol (NEAR)
- Fantom (FTM)
- The Graph (GRT)
- Harmony (ONE)
Diversification Beyond Cryptocurrencies

Cryptocurrencies, while exciting and potentially lucrative, are notoriously volatile. To build a truly resilient and long-term investment portfolio, it’s crucial to diversify beyond the digital asset realm. Spreading your investments across different asset classes mitigates risk and helps to balance potential gains and losses, creating a more stable overall financial picture. This isn’t about abandoning crypto entirely, but rather about integrating it strategically within a broader, more diversified strategy.Diversifying into traditional asset classes like stocks, bonds, and real estate can provide a crucial counterbalance to the inherent volatility of the cryptocurrency market.
These assets often exhibit different market behaviors, meaning that when one sector might be experiencing a downturn, others could be performing well. This diversification reduces the overall impact of market fluctuations on your portfolio. Think of it like building a sturdy house – you wouldn’t rely solely on one type of building material; you’d use a combination for strength and stability.
Integrating Alternative Asset Classes
Integrating traditional assets into your portfolio requires careful consideration of your risk tolerance and investment goals. A common approach is to allocate a percentage of your total investment capital to each asset class. For example, you might allocate 20% to cryptocurrencies, 40% to stocks, 30% to bonds, and 10% to real estate. This allocation would vary greatly depending on individual circumstances, risk tolerance, and investment timelines.
Someone with a higher risk tolerance and longer time horizon might allocate a larger percentage to cryptocurrencies and stocks, while someone with a lower risk tolerance and shorter time horizon might allocate more to bonds and real estate. Professional financial advice is always recommended for personalized portfolio construction.
Pros and Cons of Incorporating Traditional Assets
Before integrating traditional assets, it’s beneficial to weigh the advantages and disadvantages:
The inclusion of traditional assets offers several key benefits:
- Reduced Volatility: Traditional assets tend to be less volatile than cryptocurrencies, providing a buffer against market downturns.
- Diversification Benefits: Spreading your investments across different asset classes reduces overall portfolio risk.
- Long-Term Growth Potential: Stocks and real estate have historically provided long-term growth opportunities.
- Stability and Predictability: Bonds offer relatively stable returns and predictable income streams.
However, it’s also important to acknowledge potential drawbacks:
- Lower Potential Returns: Traditional assets generally offer lower potential returns compared to cryptocurrencies, particularly in the short term.
- Liquidity Issues: Real estate, for example, can be less liquid than stocks or cryptocurrencies, making it harder to quickly access your funds.
- Transaction Costs: Buying and selling traditional assets often involves brokerage fees and other transaction costs.
- Market Dependence: While less volatile than crypto, traditional assets are still subject to market fluctuations and economic conditions.
Rebalancing and Portfolio Monitoring
Maintaining a well-diversified cryptocurrency portfolio isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it endeavor. Market fluctuations constantly shift asset allocations, potentially derailing your carefully planned strategy. Regular rebalancing and diligent monitoring are crucial to staying on track and mitigating risk. This involves periodically adjusting your holdings to restore your target asset allocation.Regular portfolio monitoring and rebalancing are essential for maintaining your desired risk level and capitalizing on market opportunities.
Failing to do so can lead to an unintended concentration of assets in underperforming areas, reducing your overall returns and increasing your exposure to risk. Consistent monitoring allows you to adapt to changing market dynamics and proactively manage your investments.
Rebalancing a Cryptocurrency Portfolio
Rebalancing involves selling some assets that have outperformed your targets and buying more of those that have underperformed, bringing your portfolio back to its original allocation. This helps to lock in profits from winners while simultaneously reinvesting in areas you believe still hold potential. The frequency of rebalancing depends on your risk tolerance and investment strategy; some investors rebalance annually, while others do so quarterly or even monthly.
- Determine Your Target Allocation: Begin by defining the percentage of your portfolio you want allocated to each cryptocurrency (or asset class). For example, you might aim for 40% Bitcoin, 30% Ethereum, and 30% spread across other altcoins.
- Monitor Performance: Track the performance of each asset in your portfolio regularly. Use a spreadsheet, portfolio tracking software, or an exchange’s portfolio view feature. Note the current market value of each asset.
- Calculate Deviations: Compare the current allocation of each asset to your target allocation. Identify which assets have significantly deviated from your target percentages. For instance, if Bitcoin’s share has risen to 50% from your target 40%, you’ve got a 10% over-allocation.
- Rebalance Your Portfolio: Sell a portion of the over-allocated assets (e.g., Bitcoin) to bring their allocation back to your target. Use the proceeds to buy more of the under-allocated assets (e.g., Ethereum or altcoins), thereby restoring your desired balance.
- Document Transactions: Keep meticulous records of all your buy and sell transactions, including dates, quantities, and prices. This is crucial for tax purposes and for tracking your portfolio’s performance over time.
Portfolio Monitoring Strategies
Effective portfolio monitoring involves more than just checking prices daily. It requires a systematic approach that considers market trends, news events, and the overall health of the cryptocurrency market. Using various tools and resources can enhance your monitoring efforts.
- Utilize Portfolio Tracking Software: Many platforms offer tools to track your portfolio’s performance automatically, providing real-time valuations and visualizations of your asset allocation.
- Stay Informed on Market News: Regularly follow reputable cryptocurrency news sources to stay abreast of market trends, technological developments, and regulatory changes that could impact your investments.
- Set Price Alerts: Configure price alerts for your assets to receive notifications when their prices reach specific thresholds. This helps you react swiftly to significant market movements.
- Review Your Portfolio Regularly: Schedule regular reviews of your portfolio, at least monthly or quarterly, to assess its performance and identify any necessary adjustments. This consistent check-in helps ensure your strategy remains aligned with your goals.
Security and Risk Management
Protecting your diversified cryptocurrency portfolio isn’t just about making smart investments; it’s about safeguarding your assets from various threats. This section covers essential security measures and the inherent risks involved in the cryptocurrency market, providing a framework for effective risk management. Understanding these aspects is crucial for long-term success and peace of mind.Security measures are paramount for preserving your cryptocurrency holdings.
Neglecting security can lead to significant financial losses. A multi-layered approach is the most effective way to protect your investments.
Hardware Wallets and Cold Storage
Hardware wallets offer a significant upgrade in security compared to software wallets. These physical devices store your private keys offline, making them virtually immune to hacking attempts through malware or phishing scams. Examples include Ledger and Trezor, which are well-regarded for their security features and user-friendly interfaces. Cold storage, a broader term encompassing any offline storage method, further enhances security.
This could involve writing down your seed phrase (a critical recovery key) and storing it securely in a physical location, separate from your computer and other digital devices. The key is to minimize the digital footprint of your private keys. Regularly backing up your seed phrase is also vital, in case your hardware wallet is lost or damaged.
Common Risks Associated with Cryptocurrencies
The cryptocurrency market is inherently volatile, meaning prices can fluctuate dramatically in short periods. This volatility presents a significant risk, potentially leading to substantial losses if not properly managed. Regulatory changes also pose a substantial threat. Governments worldwide are still developing their approaches to regulating cryptocurrencies, and these changes can impact the value and usability of certain cryptocurrencies.
Furthermore, the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies, while beneficial in many ways, also leaves them vulnerable to hacking and theft. Exchanges and individual wallets can be targeted by sophisticated attacks, resulting in the loss of funds. Finally, scams and fraudulent projects are prevalent in the cryptocurrency space, demanding vigilance and thorough research before investing.
Risk Management Strategy
Effective risk management involves a combination of diversification and mitigation techniques. The following flowchart illustrates a strategic approach:[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would start with a box labeled “Assess Risk Tolerance and Investment Goals.” Arrows would lead to boxes labeled “Diversify Portfolio Across Multiple Cryptocurrencies and Asset Classes,” “Utilize Hardware Wallets and Cold Storage,” “Stay Informed about Market Trends and Regulatory Changes,” and “Regularly Monitor and Rebalance Portfolio.” Each of these boxes would have arrows leading to a final box labeled “Minimize Risk and Maximize Returns.”]The flowchart visually represents a systematic process.
First, understanding your risk tolerance and investment goals is fundamental. This guides the diversification strategy. Diversification spreads risk by investing in various cryptocurrencies with different market capitalizations and asset classes (like stocks or bonds). Using hardware wallets and cold storage protects your assets from hacking and theft. Staying informed about market trends and regulatory changes allows for proactive adjustments to your portfolio.
Finally, regular monitoring and rebalancing help maintain the desired asset allocation and mitigate potential losses. This iterative process ensures your portfolio remains resilient in the face of market fluctuations and emerging risks.
Tax Implications of Cryptocurrency Investments
Navigating the tax landscape of cryptocurrency investments can be complex, varying significantly depending on your location and the specifics of your transactions. Understanding these implications is crucial for responsible investing and avoiding potential legal issues. This section will provide a general overview; however, it’s essential to consult with a qualified tax professional for personalized advice tailored to your specific circumstances.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial or tax advice.Cryptocurrency transactions are generally considered taxable events in most jurisdictions. This means that profits from selling, trading, or exchanging cryptocurrencies are subject to capital gains tax, similar to the taxation of stocks or other assets. However, the exact rules and tax rates can vary widely.
Some countries may treat cryptocurrency as property, while others may classify it as a security or a commodity, each having different tax implications. Furthermore, the frequency of your trades and the holding period of your cryptocurrencies can also influence your tax liability.
Capital Gains Tax on Cryptocurrency
Capital gains tax is typically levied on the profit realized from the sale or exchange of cryptocurrencies. The profit is calculated by subtracting the original cost basis (the price you paid for the cryptocurrency) from the proceeds of the sale. For example, if you bought Bitcoin for $10,000 and sold it for $20,000, your capital gain would be $10,000, and you would owe taxes on this amount.
The applicable tax rate depends on your income level and the holding period of the asset (short-term vs. long-term gains). Short-term gains are generally taxed at a higher rate than long-term gains. The exact rates vary significantly by jurisdiction. In the United States, for instance, short-term capital gains are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, while long-term capital gains (assets held for more than one year) are taxed at preferential rates depending on your income bracket.
Tax Implications of Cryptocurrency Trading, How to diversify your cryptocurrency portfolio effectively.
Frequent trading of cryptocurrencies can lead to more complex tax calculations. Each trade, including exchanges between different cryptocurrencies, is generally considered a taxable event. This means that you will need to track each transaction and calculate the capital gains or losses for each trade separately. Accurate record-keeping is paramount to avoid underreporting your income and facing potential penalties.
For example, if you trade Bitcoin for Ethereum and later sell the Ethereum for fiat currency, both transactions will be subject to tax calculations.
Tax Reporting Requirements
Tax reporting requirements for cryptocurrency vary significantly by jurisdiction. Some countries require you to report all cryptocurrency transactions on your annual tax return, while others may have more specific reporting requirements. It’s crucial to understand the specific rules in your country and ensure you are complying with all applicable regulations. Failure to report cryptocurrency income accurately can result in significant penalties and legal consequences.
Many tax authorities now explicitly address cryptocurrency taxation in their guidelines and forms. For example, in the US, Form 8949 is used to report capital gains and losses from cryptocurrency transactions.
Examples of Tax Scenarios
Let’s consider two examples to illustrate the tax implications:Scenario 1: An investor buys 1 Bitcoin for $10,000 and sells it a year later for $20,000. Assuming a long-term capital gains tax rate of 15%, the tax liability would be $1,500 ($10,000 profit – 0.15).Scenario 2: An investor buys 1 Bitcoin for $10,000 and trades it for Ethereum, which is later sold for $15,000.
Both the Bitcoin-to-Ethereum trade and the Ethereum sale would be considered taxable events, requiring separate calculations of capital gains or losses. The tax liability will depend on the value of the Ethereum at the time of the exchange and the eventual sale price.
Resources for Further Information
For detailed and up-to-date information on cryptocurrency taxation, it’s recommended to consult official government websites and reputable financial resources. These resources can provide specific guidance based on your location and individual circumstances. Remember, tax laws are subject to change, so staying informed is vital. You should also consult with a qualified tax advisor or accountant specializing in cryptocurrency taxation.
Diversifying your cryptocurrency portfolio is a crucial step in mitigating risk and maximizing potential returns. By understanding your risk tolerance, employing appropriate asset allocation strategies, and regularly monitoring and rebalancing your portfolio, you can build a more resilient and potentially profitable investment strategy. Remember to always consider diversifying beyond cryptocurrencies into other asset classes to further reduce risk. While crypto offers exciting opportunities, a well-rounded approach ensures long-term financial health.
Don’t forget to stay informed about tax implications and security measures to protect your investments.