Analyzing the performance of different blockchain protocols. – Analyzing the performance of different blockchain protocols is crucial for understanding their strengths and weaknesses. This exploration dives into key performance indicators like transaction throughput, latency, scalability, security, and smart contract execution, comparing prominent protocols such as Ethereum, Solana, Polkadot, Algorand, and Cosmos. We’ll examine the trade-offs between decentralization and scalability, analyze different consensus mechanisms (PoW vs. PoS), and delve into the complexities of interoperability and cross-chain communication.
Prepare to gain a comprehensive understanding of what makes each blockchain tick.
We’ll use real-world examples and hypothetical scenarios to illustrate the impact of various factors on blockchain performance. Our analysis will be supported by data presented in clear, easy-to-understand tables and bullet points, making this a practical guide for anyone interested in blockchain technology, whether you’re a developer, investor, or simply curious about the future of decentralized systems.
Interoperability and Cross-Chain Communication: Analyzing The Performance Of Different Blockchain Protocols.
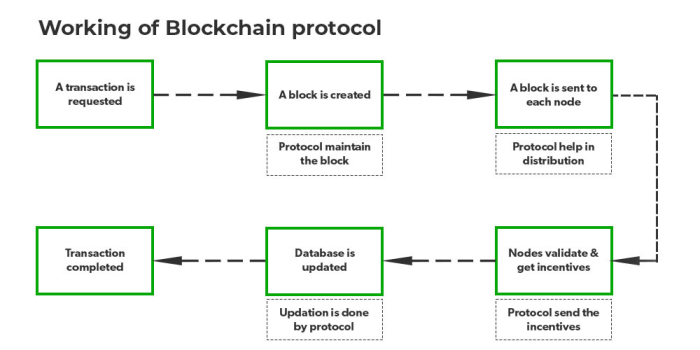
Interoperability, the ability of different blockchain networks to seamlessly communicate and exchange data, is crucial for the widespread adoption of blockchain technology. Without it, the blockchain ecosystem remains fragmented, limiting its potential for scalability and widespread utility. This section delves into the challenges and solutions associated with achieving true interoperability, exploring various approaches to cross-chain communication and proposing a novel design for a more efficient and secure protocol.
The lack of a universal standard for blockchain communication presents a significant hurdle. Different blockchains often employ varying consensus mechanisms, data structures, and programming languages, creating incompatibility. Furthermore, security concerns surrounding cross-chain transactions, such as the risk of malicious actors exploiting vulnerabilities, need careful consideration. Finally, the performance implications of cross-chain communication, including transaction speed and costs, are also important factors to address.
Challenges and Solutions Related to Interoperability
Several key challenges hinder seamless interoperability between blockchain networks. Addressing these challenges requires innovative solutions that prioritize security and efficiency. The following points highlight these challenges and potential solutions.
- Different Consensus Mechanisms: Blockchains use diverse consensus mechanisms (Proof-of-Work, Proof-of-Stake, etc.), making direct communication difficult. Solutions involve developing protocols that can translate between different consensus models or using intermediary networks that act as bridges.
- Data Structure Incompatibility: Variations in data structures and formats across blockchains create difficulties in data exchange. Standardized data formats and translation protocols are needed to overcome this hurdle.
- Security Risks: Cross-chain communication introduces new attack vectors. Solutions involve implementing robust security measures, such as secure multi-party computation and zero-knowledge proofs, to mitigate these risks.
- Scalability Issues: High transaction volumes can overwhelm cross-chain communication protocols. Solutions involve employing efficient algorithms and optimizing network infrastructure to enhance scalability.
Approaches to Cross-Chain Communication, Analyzing the performance of different blockchain protocols.
Several methods facilitate cross-chain communication, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these approaches is crucial for selecting the most suitable solution for a given application.
Atomic Swaps: Atomic swaps enable the direct exchange of assets between two different blockchains without relying on a trusted third party. This is achieved through cryptographic techniques that ensure the exchange happens atomically – either both parties receive their assets, or neither does. For example, imagine Alice holding Bitcoin on the Bitcoin blockchain and Bob holding Litecoin on the Litecoin blockchain.
An atomic swap allows them to exchange their cryptocurrencies directly without needing an intermediary service, relying solely on smart contracts and cryptographic hashing to guarantee the transaction’s integrity. The process typically involves creating a hash-locked transaction on each blockchain, and only when both transactions are confirmed do the assets get unlocked and transferred.
Bridges: Bridges act as intermediaries, facilitating the transfer of assets between different blockchains. They typically involve locking assets on one blockchain and minting equivalent tokens on another. For example, a bridge might lock ETH on the Ethereum blockchain and mint equivalent wrapped ETH (wETH) on another blockchain. While convenient, bridges introduce a degree of trust in the bridge operator, as they hold custody of the locked assets.
The security and reliability of the bridge are therefore paramount. A well-designed bridge will employ mechanisms to minimize the risk of theft or loss of funds.
Conceptual Design for a Cross-Chain Communication Protocol
An improved cross-chain communication protocol could leverage a hybrid approach combining the advantages of atomic swaps and bridges while mitigating their respective limitations. This protocol would utilize a decentralized network of validators to verify cross-chain transactions, ensuring security and minimizing the reliance on a single entity. It would also employ a standardized data format and employ optimized algorithms for efficient communication and transaction processing.
The protocol would integrate advanced cryptographic techniques, such as threshold signatures and zero-knowledge proofs, to enhance security and privacy. A robust consensus mechanism would be used to ensure the integrity and finality of cross-chain transactions, potentially using a combination of techniques to achieve high throughput and security. This hybrid approach would allow for atomic swaps where feasible and utilize bridges for more complex scenarios, providing a flexible and secure solution for cross-chain communication.
Ultimately, analyzing blockchain protocol performance reveals a complex landscape of trade-offs. No single protocol excels in every area; each has its strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these nuances is key to choosing the right blockchain for a specific application. This analysis provides a framework for evaluating future protocols and contributes to the ongoing conversation about the evolution and improvement of decentralized technologies.
By understanding the intricacies of transaction speeds, scalability solutions, security models, and smart contract capabilities, we can collectively shape a more efficient and secure blockchain ecosystem.
Check what professionals state about Understanding the risks and rewards of investing in altcoins. and its benefits for the industry.
Obtain access to How does Dogecoin’s price fluctuate in relation to Bitcoin and other major cryptocurrencies? to private resources that are additional.