The potential use of blockchain technology in supply chain traceability. – The potential use of blockchain technology in supply chain traceability is revolutionizing how we track goods. Imagine a world where every product’s journey, from origin to consumer, is transparent and verifiable. This isn’t science fiction; blockchain technology, with its secure and immutable ledger, is making this a reality. We’ll explore how this innovative technology enhances transparency, efficiency, and trust across various industries.
This exploration will cover the core principles of blockchain, its applications in different sectors (like food and pharmaceuticals), and the technical aspects of implementation. We’ll also address potential challenges, including security and scalability, and look towards the future of blockchain in supply chain management, envisioning a more sustainable and ethical industry.
Technical Aspects and Implementation of Blockchain Solutions
Building a successful blockchain-based supply chain system requires careful consideration of various technical aspects. Choosing the right blockchain type, integrating necessary components, and planning the implementation process are crucial for achieving the desired level of traceability and efficiency. This section delves into the key technical considerations.
Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
The choice of consensus mechanism significantly impacts a blockchain’s performance and security. Different mechanisms offer varying trade-offs between speed, scalability, and energy consumption. This makes the selection process crucial, depending on the specific needs of the supply chain.
- Proof-of-Work (PoW): PoW, famously used by Bitcoin, relies on miners competing to solve complex cryptographic puzzles. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add the next block to the chain and receives a reward. While highly secure, PoW is energy-intensive and can be slow, making it less ideal for high-throughput supply chain applications requiring rapid transaction processing.
Find out about how Exploring the potential of blockchain technology in the supply chain. can deliver the best answers for your issues.
- Proof-of-Stake (PoS): PoS is a more energy-efficient alternative. Instead of solving puzzles, validators are selected based on the amount of cryptocurrency they “stake,” or hold. The selected validator proposes and validates blocks, earning rewards. PoS generally offers faster transaction speeds and better scalability than PoW, making it a more suitable option for many supply chain use cases.
- Other Consensus Mechanisms: Other mechanisms like Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) and Raft are also used. These are often preferred for private or permissioned blockchains, offering high throughput and low latency, but potentially sacrificing the decentralization aspect present in public blockchains like those using PoW or PoS.
Key Technological Components
Several technological components are essential for a robust blockchain-based supply chain system. These components work together to ensure data integrity, security, and efficient information sharing across the network.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Smart contracts automate various supply chain processes, such as payments, product tracking, and quality checks, enhancing transparency and efficiency.
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): APIs facilitate seamless communication between the blockchain system and existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and other applications within the supply chain. They enable the integration of blockchain technology into the pre-existing infrastructure.
- Data Storage: Secure and reliable data storage is paramount. Blockchain itself stores transactional data, but additional data (e.g., product images, certifications) might need to be stored off-chain, with mechanisms to ensure data integrity and linkage to the blockchain records. This often involves using decentralized storage solutions or secure cloud storage.
Integrating Blockchain into Existing Supply Chain Infrastructure, The potential use of blockchain technology in supply chain traceability.
Integrating blockchain into an existing supply chain involves a phased approach, requiring careful planning and execution.
Find out about how Exploring the use of blockchain technology in the education sector. can deliver the best answers for your issues.
- Assessment and Planning: Identify the specific supply chain processes to be improved with blockchain, define the scope of implementation, and select appropriate technology partners.
- Proof-of-Concept (POC): Develop a small-scale pilot project to test the feasibility and efficacy of the blockchain solution in a real-world setting. This helps identify and address potential challenges early on.
- System Design and Development: Design the blockchain architecture, including the selection of consensus mechanism, smart contracts, and data storage solutions. Develop the necessary software and integrate it with existing systems using APIs.
- Testing and Deployment: Thoroughly test the system to ensure its functionality, security, and scalability. Deploy the system gradually, starting with a limited set of participants, and expanding as needed.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Continuously monitor the system’s performance and address any issues that arise. Regular updates and maintenance are essential to ensure the long-term success of the blockchain implementation.
Challenges and Considerations for Blockchain Adoption: The Potential Use Of Blockchain Technology In Supply Chain Traceability.
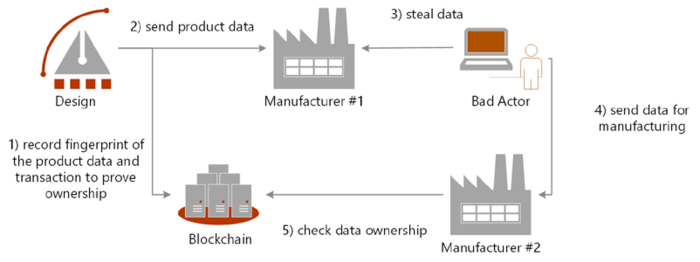
Implementing blockchain technology in supply chains offers significant advantages, but it’s not without its hurdles. Several challenges related to security, scalability, and regulatory compliance need careful consideration before widespread adoption can be achieved. Addressing these issues proactively is crucial for realizing the full potential of blockchain in enhancing supply chain transparency and efficiency.
Security Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Blockchain’s inherent security features, such as cryptographic hashing and distributed ledger technology, offer strong protection against data tampering and fraud. However, vulnerabilities still exist, particularly at the edges of the blockchain system. For example, compromised private keys can allow malicious actors to alter transaction records, while vulnerabilities in smart contracts can lead to unintended consequences. Mitigation strategies include robust key management systems, regular security audits of smart contracts, and the implementation of multi-signature authorization for critical transactions.
Furthermore, integrating blockchain with other security technologies, such as intrusion detection systems and encryption protocols, provides an additional layer of protection. Companies should also invest in employee training programs to increase awareness of security best practices and potential threats.
Scalability Issues in Blockchain-Based Supply Chains
Blockchain’s scalability can be a significant concern when dealing with the massive data volumes typical of global supply chains. Processing numerous transactions across a large network can lead to slow transaction speeds and high network fees. For example, a large retailer managing millions of products and transactions daily might experience significant delays in tracking and updating information on the blockchain.
Solutions include exploring different consensus mechanisms (like Proof-of-Stake instead of Proof-of-Work), utilizing sharding techniques to partition the blockchain into smaller, more manageable segments, and employing off-chain solutions to handle large volumes of data before committing summaries to the blockchain. Efficient data management strategies and careful selection of appropriate blockchain platforms are also vital for mitigating scalability issues.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations for Blockchain Adoption
The regulatory landscape for blockchain technology is still evolving and varies significantly across different jurisdictions. Data privacy regulations, such as GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California, pose challenges for organizations sharing sensitive supply chain data on a blockchain. Furthermore, the legal enforceability of smart contracts and the ownership of data on a blockchain are still areas of ongoing debate and legal clarification.
Companies must carefully navigate these regulatory complexities by ensuring compliance with all applicable laws and regulations in the regions where they operate. Proactive engagement with regulators and legal experts is crucial for mitigating legal risks and fostering a supportive regulatory environment for blockchain adoption in supply chains.
Future Trends and Developments
The rapid evolution of blockchain technology promises to significantly enhance supply chain traceability beyond its current capabilities. Emerging trends are not only improving the technology itself but also expanding its applications and impact across various sectors. These advancements are paving the way for a more transparent, efficient, and sustainable supply chain ecosystem.The convergence of blockchain with other innovative technologies is driving the next wave of improvements in supply chain traceability.
This synergy leads to more robust, secure, and scalable solutions.
Decentralized Identifiers and Interoperability
Decentralized identifiers (DIDs) offer a promising solution to the interoperability challenges currently facing blockchain-based supply chain systems. Different blockchain platforms often operate in silos, hindering seamless data sharing. DIDs, however, provide a mechanism for verifiable digital identities that can traverse different blockchain networks, allowing for a more unified and comprehensive view of the supply chain. Imagine a scenario where a shipment of coffee beans travels through multiple countries, each with its own blockchain system tracking different aspects like origin, processing, and transportation.
DIDs enable each stage to be verified and linked seamlessly, providing complete transparency across the entire journey, regardless of the underlying blockchain platform. This enhanced interoperability simplifies data exchange and reduces the complexities associated with integrating various systems.
Blockchain’s Impact on Supply Chain Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
Blockchain technology is increasingly being leveraged to promote sustainable and ethical practices within supply chains. By providing immutable records of a product’s journey, from raw material sourcing to final delivery, blockchain facilitates the verification of ethical sourcing claims. For example, a consumer could scan a QR code on a garment and trace its origin, verifying that the cotton was sustainably grown and the garment produced under fair labor conditions.
This transparency empowers consumers to make informed choices, supporting businesses committed to ethical and sustainable practices while holding those that are not accountable. Furthermore, the traceability provided by blockchain helps to identify and mitigate environmental risks, promoting sustainable resource management throughout the supply chain. Tracking carbon emissions at each stage, for instance, allows for better management and reduction strategies.
A Vision for the Future of Blockchain-Enabled Supply Chain Management
The future of blockchain in supply chain management points towards a fully integrated, transparent, and resilient ecosystem. Imagine a world where every product carries a digital passport, containing its complete history, from origin to consumer. This digital passport would be accessible to all stakeholders – producers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and consumers – providing complete visibility and trust. This would not only improve efficiency and reduce fraud but also empower consumers to make informed decisions based on the ethical and environmental impact of their purchases.
Real-time tracking of goods will minimize disruptions, optimize logistics, and improve responsiveness to market demands. For instance, a sudden surge in demand for a particular product could be met efficiently due to real-time visibility of inventory levels across the entire supply chain. This scenario showcases a future where blockchain technology empowers a more responsible, efficient, and sustainable global trade system.
The resulting increased transparency and accountability would ultimately benefit all participants, fostering trust and collaboration across the entire supply chain.
Blockchain technology offers a powerful solution to long-standing supply chain challenges. By providing enhanced traceability and transparency, it fosters trust, improves efficiency, and ultimately benefits both businesses and consumers. While challenges remain, the potential for transformative change is undeniable. As blockchain technology matures and adoption increases, we can expect to see even more innovative applications that will reshape the future of supply chain management, leading to a more efficient, secure, and sustainable global economy.